Alpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri is the closest star system to the Sun, located approximately 4.37 light-years away. It is a triple star system consisting of two sun-like stars, Alpha Centauri A and B, and a red dwarf, Proxima Centauri, which is the nearest individual star to Earth.
Source: earthsky.org
APODs including "Alpha Centauri"
Sirius: The Brightest Star in the Night
02/09/1996
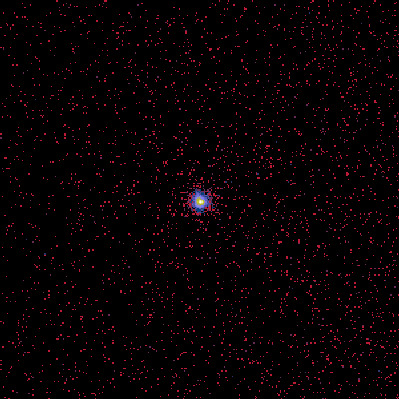
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Intrinsically, Sirius is over 20 times brighter than our Sun and over twice as massive. As Sirius is 8.7 light years distant, it is not the closest star system -- the Alpha Centauri system holds this distinction. Sirius is called the Dog Star because of its prominence in the constellation of Canis Majoris (Big Dog). In 1862, Sirius was discovered to be a binary star system with a companion star, Sirius B, 10,000 times dimmer than the bright primary, Sirius A. Sirius B was the first white dwarf star discovered, a type of star first understood by Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar in 1930. While studying Sirius in 1718, Edmond Halley discovered that stars move with respect to each other. The Sirius system is shown above captured in X-ray light.