Black Hole
A black hole is an astronomical object whose gravity is so strong that nothing—even light—can escape from within its event horizon. It forms when a massive star’s core collapses or through other processes, and may have an accretion disk of infalling matter that emits radiation. Supermassive black holes at galaxy centers influence stellar orbits, and mergers produce gravitational waves.
Source: nasa.gov
APODs including "Black Hole"
Black Holes Signature From Advective Disks Research Credit:
15/01/1997
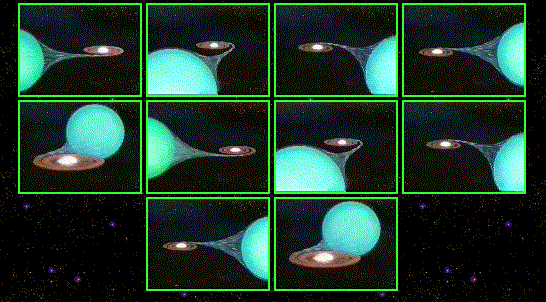
What does a black hole look like? If alone, a black hole would indeed appear quite black, but many black hole candidates are part of binary star systems. So how does a black hole binary system look different from a neutron star binary system? The above drawings indicate it is difficult to tell! Recent theoretical work, however, has provided a new way to tell them apart: advective accretion flows (ADAFs). A black hole system so equipped would appear much darker than a similar neutron star system. The difference is caused by the hot gas from the ADAF disk falling through the event horizon of the black hole and disappearing - gas that would have emitted much light were the central object only a neutron star. Recent observations of the soft X-ray transient V404 Cyg has yielded a spectrum much like an ADAF onto a black hole - and perhaps brighter than allowable from an ADAF onto a neutron star.