Black Hole
A black hole is an astronomical object whose gravity is so strong that nothing—even light—can escape from within its event horizon. It forms when a massive star’s core collapses or through other processes, and may have an accretion disk of infalling matter that emits radiation. Supermassive black holes at galaxy centers influence stellar orbits, and mergers produce gravitational waves.
Source: nasa.gov
APODs including "Black Hole"
X-Ray Cygnus A
10/11/2000
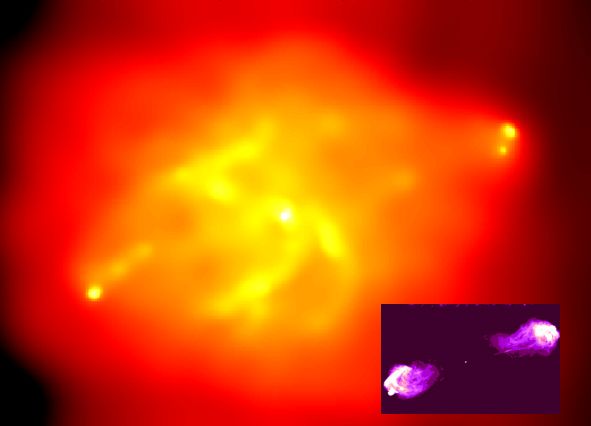
Amazingly detailed, this false-color x-ray image is centered on the galaxy Cygnus A. Recorded by the orbiting Chandra Observatory, Cygnus A is seen here as a spectacular high energy x-ray source. But it is actually more famous at the low energy end of the electromagnetic spectrum as one of the brightest celestial radio sources. Merely 700 million light-years distant, Cygnus A is the closest powerful radio galaxy and the false-color radio image (inset right) shows remarkable similarity to Chandra's x-ray view. Central in both pictures, the center of Cygnus A shines brightly while emission extends 300,000 light-years to either side along the same axis. Near light speed jets of atomic particles produced by a massive central black hole are believed to cause the emission. In fact, the x-ray image reveals "hot spots" suggestive of the locations where the particle jets are stopped in surrounding cooler, denser gas. The x-ray image also shows that the jets have cleared out a huge cavity in the surrounding gas. Bright swaths of emission within the cavity likely indicate x-ray hot material ... swirling toward the central black hole.