Black Hole
A black hole is an astronomical object whose gravity is so strong that nothing—even light—can escape from within its event horizon. It forms when a massive star’s core collapses or through other processes, and may have an accretion disk of infalling matter that emits radiation. Supermassive black holes at galaxy centers influence stellar orbits, and mergers produce gravitational waves.
Source: nasa.gov
APODs including "Black Hole"
Active Galaxy Centaurus A
10/01/2008
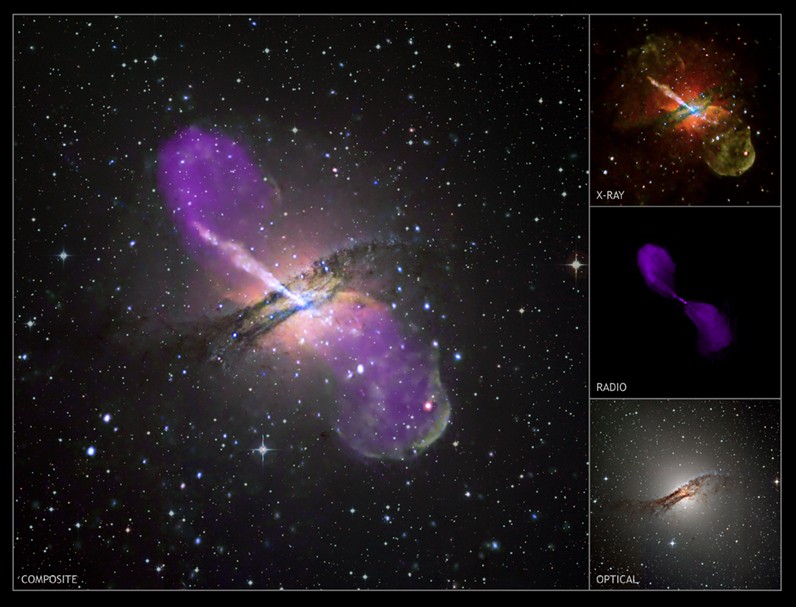
A mere 11 million light-years away, Centaurus A is a giant elliptical galaxy - the closest active galaxy to Earth. This remarkable composite view of the galaxy combines image data from the x-ray ( Chandra), optical(ESO), and radio(VLA) regimes. Centaurus A's central region is a jumble of gas, dust, and stars in optical light, but both radio and x-ray telescopes trace a remarkable jet of high-energy particles streaming from the galaxy's core. The cosmic particle accelerator's power source is a black hole with about 10 million times the mass of the Sun coincident with the x-ray bright spot at the galaxy's center. Blasting out from the active galactic nucleus toward the upper left, the energetic jet extends about 13,000 light-years. A shorter jet extends from the nucleus in the opposite direction. Other x-ray bright spots in the field are binary star systems with neutron stars or stellar mass black holes. Active galaxy Centaurus A is likely the result of a merger with a spiral galaxy some 100 million years ago.