European Southern Observatory
The European Southern Observatory (ESO) is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1962 and supported by 16 member states and host country Chile. ESO designs, builds, and operates some of the world's most advanced ground-based astronomical observatories—such as La Silla, Paranal (home to the Very Large Telescope and other survey instruments), and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA)—and is currently constructing the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT).
Source: eso.org
APODs including "European Southern Observatory"
The Helix Nebula from La Silla Observatory
03/03/2009
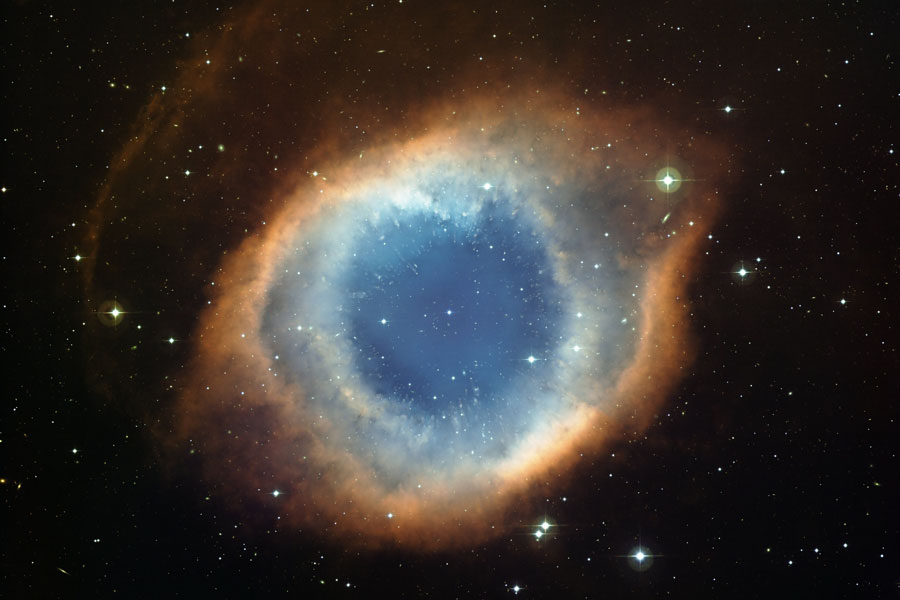
Will our Sun look like this one day? The Helix Nebula is one of brightest and closest examples of a planetary nebula, a gas cloud created at the end of the life of a Sun-like star. The outer gasses of the star expelled into space appear from our vantage point as if we are looking down a helix. The remnant central stellar core, destined to become a white dwarf star, glows in light so energetic it causes the previously expelled gas to fluoresce. The Helix Nebula, given a technical designation of NGC 7293, lies about 700 light-years away towards the constellation of Aquarius and spans about 2.5 light-years. The above picture was taken by the Wide Field Imager on the 2.2-meter Telescope at the European Southern Observatory's La Silla Observatory. A close-up of the inner edge of the Helix Nebula shows complex gas knots of unknown origin.