False Color
A method of representing data where colors are assigned to specific ranges of values, often used in astronomical imaging to visualize wavelengths outside the visible spectrum.
Source: earthobservatory.nasa.gov
APODs including "False Color"
A Sky Full Of Hydrogen
01/03/1998
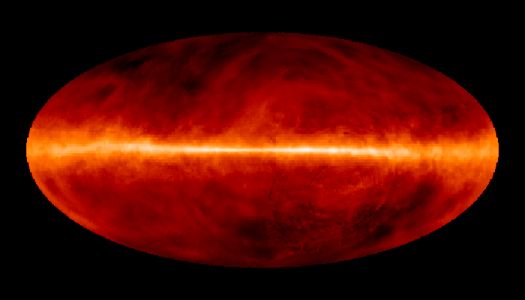
Interstellar space is filled with extremely tenuous clouds of gas which are mostly Hydrogen. The neutral hydrogen atom (HI in astronomer's shorthand) consists of 1 proton and 1 electron. The proton and electron spin like tops but can have only two orientations; spin axes parallel or anti-parallel. It is a rare event for Hydrogen atoms in the interstellar medium to switch from the parallel to the anti-parallel configuration, but when they do they emit radio waves with a wavelength of 21 centimeters (about 8 inches) and a corresponding frequency of exactly 1420 MHz. Tuned to this frequency radio telescopes have mapped the neutral Hydrogen in the sky. The above image represents such an all-sky HI survey with the plane of our Milky Way Galaxy running horizontally through the center. In this false color image no stars are visible, just diffuse clouds of gas tens to hundreds of light years across which cluster near the plane. The gas clouds seem to form arching, looping structures, stirred up by stellar activity in the galactic disk.