False Color
A method of representing data where colors are assigned to specific ranges of values, often used in astronomical imaging to visualize wavelengths outside the visible spectrum.
Source: earthobservatory.nasa.gov
APODs including "False Color"
Cygnus Trio
07/11/2008
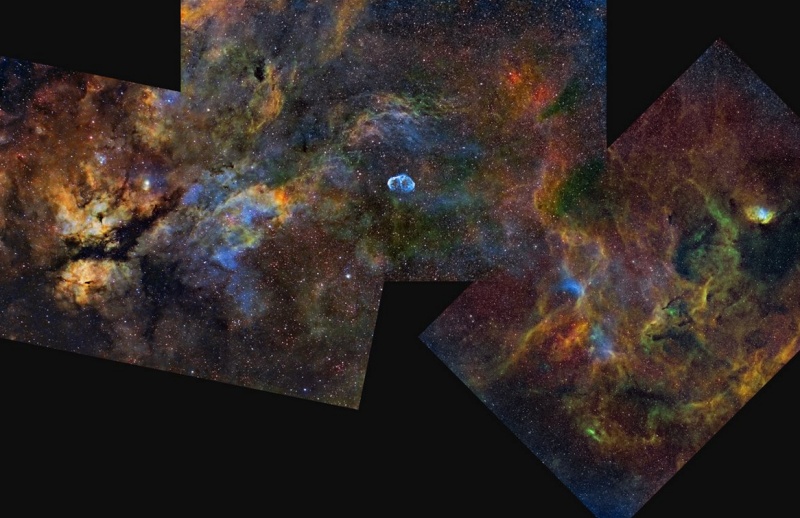
In this colorful mosaic, filaments of gas and dust span some 9 degrees across central Cygnus, a nebula rich constellation along the northern Milky Way. A trio of nebulae with popular names highlights the beautiful skyscape - the Butterfly, the Crescent, and the Tulip. At left, the Butterfly Nebula (IC 1318), lies near bright star Gamma Cygni. The Butterfly's expansive, glowing, wing-shaped gas clouds are divided by a dark dust lane. Near center, the Crescent Nebula (NGC 6888) is more compact, a cosmic bubble with a bright edge blown by winds from a massive Wolf-Rayet star. On the right is the Tulip Nebula (Sh2-101), a small emission region shaped like a blossoming flower viewed from the side. All are within a few thousand light-years of the Sun in the Orion spiral arm of our galaxy. The gorgeous mosaic is presented in false color, constructed from image data recorded through narrow band filters. The range of colors was created by a mapping of emission from hydrogen, sulfur and oxygen atoms in the nebula to red, green, and blue hues. Take a survey on Aesthetics and Astronomy.