Galactic Center
The Galactic Center is the rotational center of the Milky Way galaxy, located approximately 25,000 light-years from Earth in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius. It is a densely populated region containing a supermassive black hole known as Sagittarius A*, surrounded by a high concentration of stars, gas, and dust.
Source: nasa.gov
APODs including "Galactic Center"
Magnetar In The Sky
02/10/1998
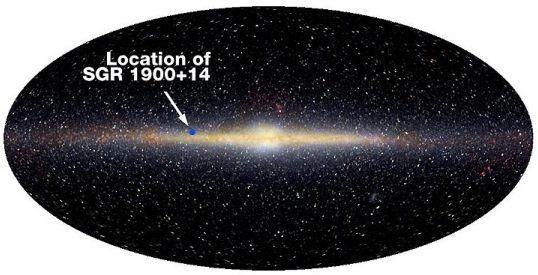
Indicated on this infrared image of the galactic center region is the position of SGR 1900+14 - the strongest known magnet in the galaxy. SGR 1900+14 is believed to be a city-sized, spinning, super-magnetic neutron star, or Magnetar. How strong is a Magnetar's magnetic field? The Earth's magnetic field which deflects compass needles is measured to be about 1 Gauss, the strongest fields sustainable in Earth-based laboratories are about 100,000 Gauss, yet the Magnetar's monster magnetic field is estimated to be 1,000,000,000,000,000 Gauss. A magnet this strong, located at about half the distance to the Moon would easily erase your credit cards and suck pens out of your pocket. From a distance of about 20,000 light-years, SGR 1900+14 recently generated a powerful flash of gamma-rays detected by many spacecraft. That blast of high-energy radiation is now known to have had a measurable effect on Earth's ionosphere. At the surface of the Magnetar, its powerful magnetic field is thought to buckle and shift the neutron star crust generating the intense gamma-ray flares.