Galactic Plane
The Galactic Plane is the plane in which the majority of a disk-shaped galaxy's mass lies. In the case of the Milky Way, it is the plane of the galaxy's disk, encompassing the spiral arms, stars, gas, and dust. This plane is used as the reference for the galactic coordinate system.
Source: asd.gsfc.nasa.gov
APODs including "Galactic Plane"
Supernova Remnant Imaged in Gamma Rays
05/11/2004
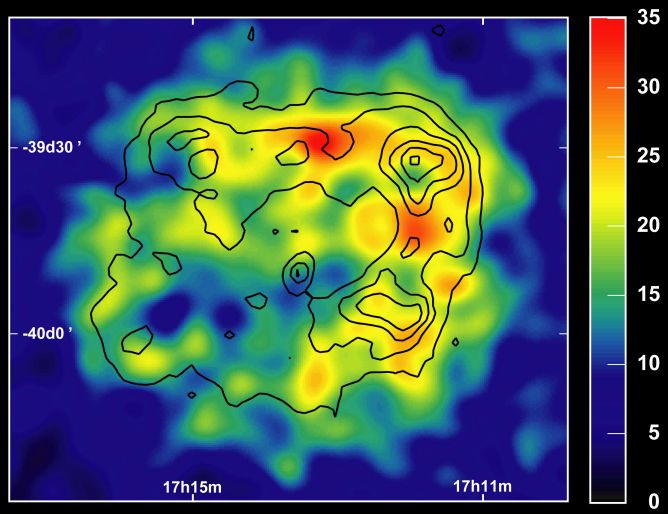
Gamma rays are the most energetic form of light. With up to a billion times the energy of ordinary "medical" x-rays, they easily penetrate telescope lenses and mirrors, making it very difficult to create gamma-ray images of cosmic sources. Still, an array of large telescopes designed to detect gamma-ray induced atmospheric flashes - the HESS (High Energy Stereoscopic System) experiment - has produced this historic, resolved image of a supernova remnant at extreme gamma-ray energies. Astronomers note that the premier gamma-ray view of the expanding stellar debris cloud is clearly similar to x-ray images of the remnant and convincingly supports the idea that these sites of powerful shock waves are also sources of cosmic rays within our galaxy. The gamma-ray intensity is color-coded in the picture, shown with dark contour lines that trace levels of x-ray emission from the object. At an estimated distance of 3,000 light-years, the supernova remnant measures about 50 light-years across and lies near the galactic plane.