Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA robotic spacecraft launched on June 18, 2009. It operates in a low polar orbit around the Moon and is mapping the lunar surface in unprecedented detail, measuring topography, radiation, temperature, and resources. Its data help identify safe landing sites, locate water ice in shadowed regions, and support future human and robotic exploration.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter"
A Colorful Side of the Moon
18/11/2011
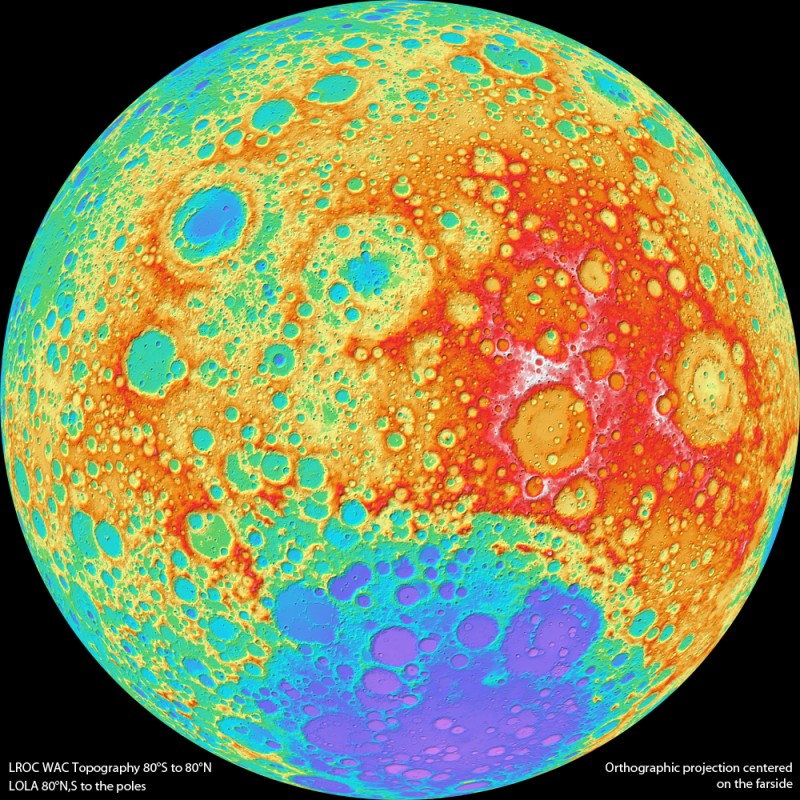
This colorful topographical map of the Moon is centered on the lunar farside, the side not seen from planet Earth. That view is available to the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter though, as the spacecraft's wide angle camera images almost the entire lunar surface every month. Stereo overlap of the imaging has allowed the computation of topographical maps with coverage between 80 degrees north and south latitude. The results have about a 300 meter resolution on the lunar surface and 10 to 20 meter elevation accuracy. Data closer to the north and south poles is filled in using the orbiter's laser altimeter. In this map, white, red, green, and purple represent progressively lower elevations. In fact, the large circular splotch tending to purple hues at the bottom is the farside's South Pole-Aitken Basin. About 2500 kilometers in diameter and over 12 kilometers deep, it is one of the largest impact basins in the Solar System.