Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the seventh largest in the Solar System. A cold, dusty desert world with a thin atmosphere (mostly CO₂), the planet features extinct volcanoes, deep canyons, polar ice caps, and seasons. Mars has two small moons (Phobos and Deimos), a day just over 24 hours long, and a year lasting about 687 Earth days. It is a prime focus of robotic exploration and studies about past water and habitability.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Mars"
Early Microscopic Life on Mars?
07/08/1996
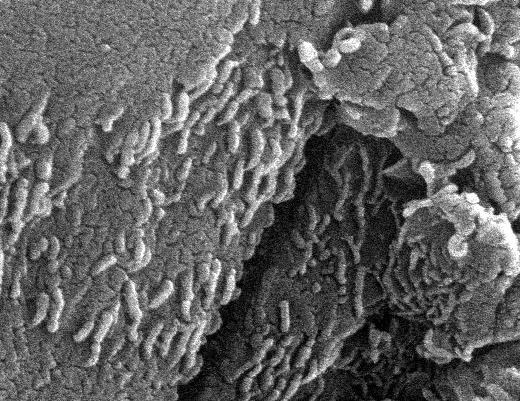
Today a team of NASA and Stanford scientists announced the discovery of strong circumstantial evidence that microscopic life once existed on Mars. Dr. David McKay, Dr. Everett Gibson, and Kathie Thomas-Keprta of Lockheed-Martin, all from (NASA /JSC), and Dr. Richard Zare (Stanford) have led a team that has found chemical evidence for past life on Mars - including what they interpret as possible microscopic fossil remains (tube-like structures pictured above) - in a meteorite thought to have originated on Mars. A small fraction of the many meteorites that fall to Earth from space have composition similar to the Martian surface. Many scientists believe that these meteorites are indeed Martian rocks that have been catapulted into space during a catastrophic event on Mars, such as an asteroid impact. The escaped rocks would then circle the inner Solar System, some of them falling to Earth. The meteorite containing the evidence landed on Earth 13,000 years ago, but may indicate a life-form that existed on Mars billions of years ago. The team's findings will be published in the August 16 issue of Science Magazine. Even skeptical scientists look forward to future research confirming or refuting these exciting claims.