Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the seventh largest in the Solar System. A cold, dusty desert world with a thin atmosphere (mostly CO₂), the planet features extinct volcanoes, deep canyons, polar ice caps, and seasons. Mars has two small moons (Phobos and Deimos), a day just over 24 hours long, and a year lasting about 687 Earth days. It is a prime focus of robotic exploration and studies about past water and habitability.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Mars"
Southern Mars
03/12/1999
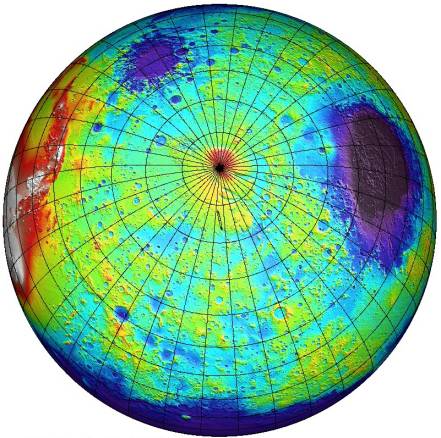
This topographical map of the southern hemisphere of Mars was generated using data from the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA). Flying on the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft, MOLA has bounced a laser beam off the Martian surface over 200,000,000 times producing a wealth of detailed elevation measurements. The MOLA measurements have been color-coded so, for example, the white areas at left are the highest elevations in the southern Tharsis region and not snow-covered peaks. These areas are more than 6 kilometers above the hypothetical Martian "sea-level". Likewise, deep blues and purples are not water oceans but correspond to the lowest elevations (more than 4 kilometers below "sea-level"), like those found within the giant Hellas impact basin at right. In fact, liquid water is not present on Mars' surface today, but may have been in the past. NASA's Mars Polar Lander spacecraft is scheduled to embark on an investigation of the role of water in the climate history of the Red Planet. The lander is targeted to touch down within the long, thin ellipse indicated here just below the Martian South Pole today at 20:00 UTC.