Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the seventh largest in the Solar System. A cold, dusty desert world with a thin atmosphere (mostly CO₂), the planet features extinct volcanoes, deep canyons, polar ice caps, and seasons. Mars has two small moons (Phobos and Deimos), a day just over 24 hours long, and a year lasting about 687 Earth days. It is a prime focus of robotic exploration and studies about past water and habitability.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Mars"
Magnified Mars
06/02/2004
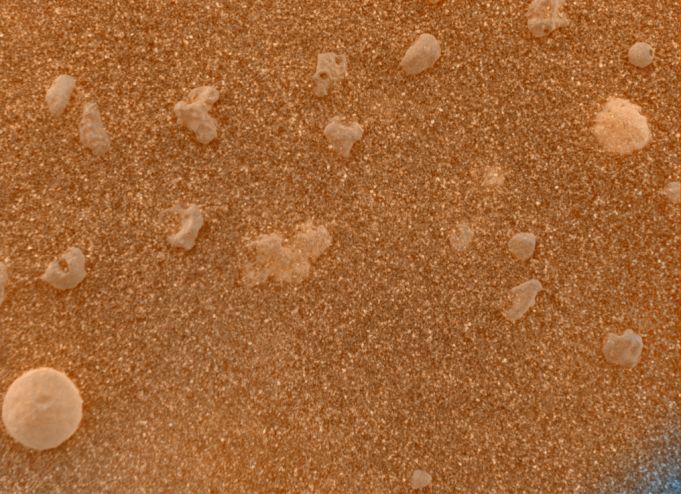
At first glance, this sharp, color close-up gives the strong impression of pebbles strewn over a sandy beach. But the picture is one of the first microscopic images of another planet, captured by the Opportunity rover on its tenth sol on the martian surface at Meridiani Planum. The patch of soil measures about 3 centimeters (1.2 inches) across. It is shown in shades approximating what the eye might see, obtained by combining pictures of the soil with and without the microscopic imager's orange-tinted dust cover in place. Searching for evidence of past water on Mars, researchers note that both volcanic and water-related accretion processes could have produced the striking circular grain at the lower left. However, other investigations now indicate the soil near the lander contains olivine, an iron-bearing mineral common in volcanic rocks, while a signature of the iron mineral hematite was found in soil around a nearby rocky outcrop. On planet Earth, hematite often forms in association with liquid water.