Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the seventh largest in the Solar System. A cold, dusty desert world with a thin atmosphere (mostly CO₂), the planet features extinct volcanoes, deep canyons, polar ice caps, and seasons. Mars has two small moons (Phobos and Deimos), a day just over 24 hours long, and a year lasting about 687 Earth days. It is a prime focus of robotic exploration and studies about past water and habitability.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Mars"
MAVEN at Mars
26/09/2014
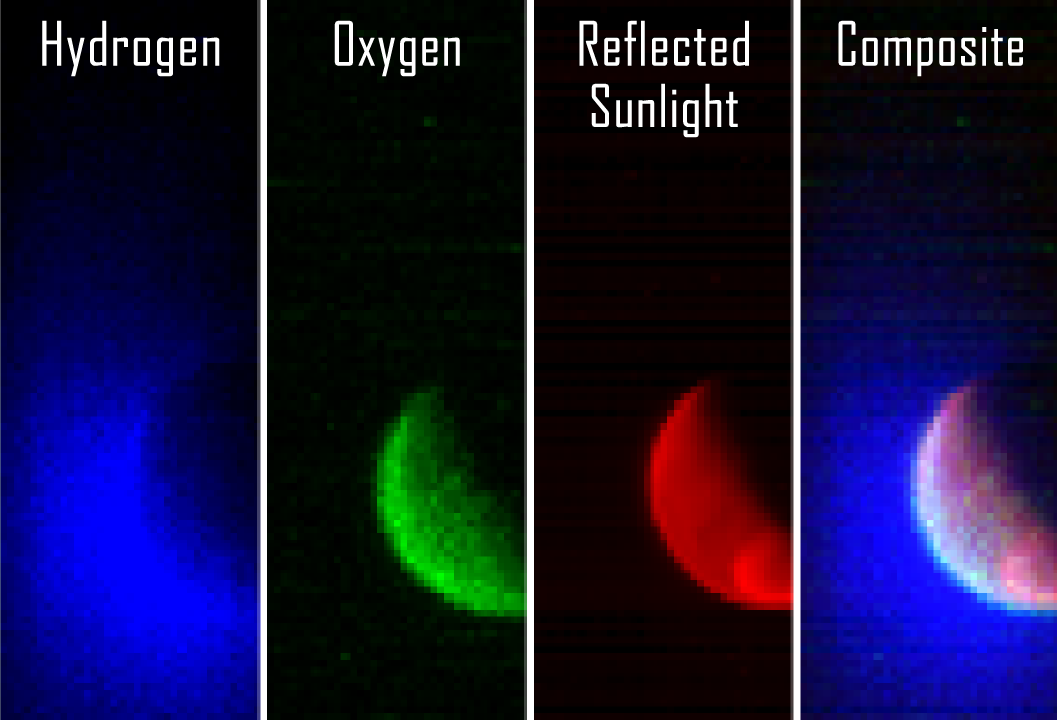
Launched on November 18, 2013, the MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN) spacecraft completed its interplanetary voyage September 21, captured into a wide, elliptical orbit around Mars. MAVEN's imaging ultraviolet spectrograph has already begun its planned exploration of the Red Planet's upper atmosphere, acquiring this image data from an altitude of 36,500 kilometers. In false color, the three ultraviolet wavelength bands show light reflected from atomic hydrogen (in blue), atomic oxygen (in green) and the planet's surface (in red). Low mass atomic hydrogen is seen to extend thousands of kilometers into space, with the cloud of more massive oxygen atoms held closer by Mars' gravity. Both are by products of the breakdown of water and carbon dioxide in Mars' atmosphere and the MAVEN data can be used to determine the rate of water loss over time. In fact, MAVEN is the first mission dedicated to exploring Mars' tenuous upper atmosphere, ionosphere and interactions with the Sun and solar wind. But the most recent addition to the fleet of spacecraft from planet Earth now in martian orbit is MOM.