Nebula
A nebula is a giant cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and cosmic dust situated between stars in the interstellar medium. Nebulae serve as sites of stellar birth and death—including emission nebulae that glow from ionized gas, reflection nebulae that scatter starlight, and dark nebulae that obscure background stars.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Nebula"
M42: Orion Nebula Mosaic
21/11/1995
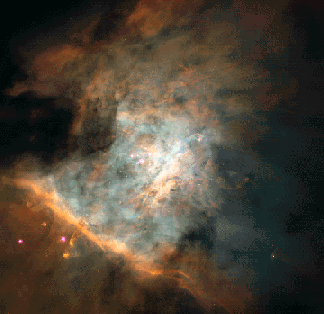
The Great Nebula in Orion is one of the most interesting of all astronomical nebulae known. Here fifteen pictures from the Hubble Space Telescope have been merged to show the great expanse and diverse nature of the nebula. In addition to housing a bright open cluster of stars known as the Trapezium, the Orion Nebula contains many stellar nurseries. These nurseries contain hydrogen gas, hot young stars, proplyds, and stellar jets spewing material at high speeds. Much of the filamentary structure visible in this image are actually shock waves - fronts where fast moving material encounters slow moving gas. Some shock waves are visible near one of the bright stars in the lower left of the picture. The Orion Nebula is located in the same spiral arm of our Galaxy as is our Sun. It takes light about 1500 years to reach us from there.