Nebula
A nebula is a giant cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and cosmic dust situated between stars in the interstellar medium. Nebulae serve as sites of stellar birth and death—including emission nebulae that glow from ionized gas, reflection nebulae that scatter starlight, and dark nebulae that obscure background stars.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Nebula"
Vela Supernova Remnant in X-ray
12/06/1996
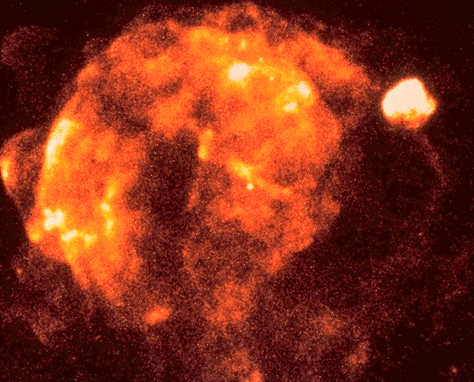
What happens when a star explodes? A huge fireball of hot gas shoots out in all directions. When this gas slams into the existing interstellar medium, it heats up so much it glows in X-rays. The above picture by the ROSAT satellite has captured some of these X-rays and shown -- for the first time -- the Vela supernova explosion was roughly spherical. Non-uniformity of the interstellar medium causes Vela's appearance to be irregular. The size of this X-ray emitting spherical shell is immense - 230 light years across, covering over 100 times the sky-area of the full Moon. The supernova that created this nebula occurred about 1500 light years away and about 11,000 years ago. Coincidently, a completely different supernova shell can also be seen in X-rays in this picture! It is visible as the bright patch near the upper right. This Puppis supernova remnant nebula is actually about four times farther than the Vela nebula.