Nebula
A nebula is a giant cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and cosmic dust situated between stars in the interstellar medium. Nebulae serve as sites of stellar birth and death—including emission nebulae that glow from ionized gas, reflection nebulae that scatter starlight, and dark nebulae that obscure background stars.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Nebula"
Superbubbles in the LMC
03/07/1996
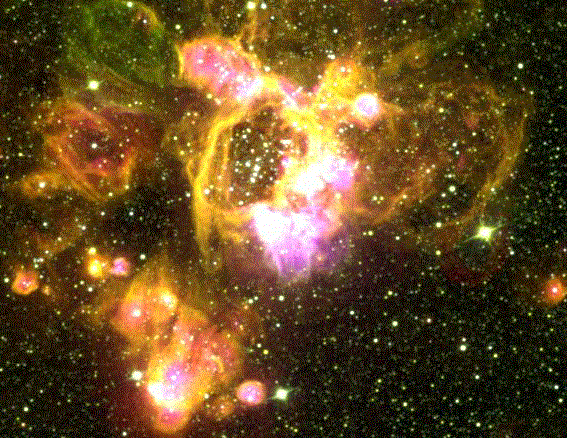
Why is there a hole in the center of this nebula? A leading explanation is that it is caused by the stellar winds from the stars that live there. Stars - including the Sun - expel electrons, protons, and other charged ions in a steady stream - the stellar wind. The wind ions push out the normal hydrogen and helium gas found glowing in the nebula. This star forming region is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud. This picture is a composite of three separate photographs, each sensitive to only one specific color of light - a color that distinguishes a specific chemical element. It is currently not known why stars emit a stellar wind.