Nebula
A nebula is a giant cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and cosmic dust situated between stars in the interstellar medium. Nebulae serve as sites of stellar birth and death—including emission nebulae that glow from ionized gas, reflection nebulae that scatter starlight, and dark nebulae that obscure background stars.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Nebula"
NGC 604: Giant Stellar Nursery in M33
16/08/1996
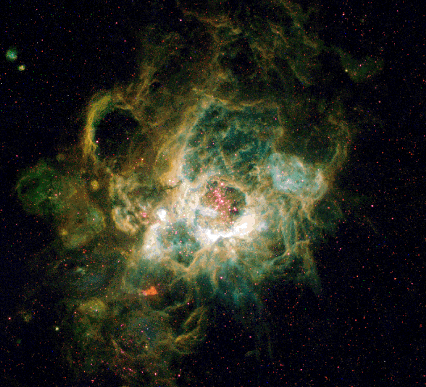
The nebula cataloged as NGC 604 is a giant star forming region, 1500 light years across, in the nearby spiral galaxy, M33. Seen here in a snapshot by the Hubble Space Telescope, over 200 newly formed, hot, massive, stars are scattered within a cavern-like, gaseous, interstellar cloud. The stars irradiate the gas with energetic ultraviolet light stripping electrons from atoms and exciting them - producing a characteristic nebular glow. The details of the nebula's structure hold clues to the mysteries of star formation and its effect on the evolution of galaxies.