Nebula
A nebula is a giant cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and cosmic dust situated between stars in the interstellar medium. Nebulae serve as sites of stellar birth and death—including emission nebulae that glow from ionized gas, reflection nebulae that scatter starlight, and dark nebulae that obscure background stars.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Nebula"
Starburst Ring in Galaxy NGC 1317 Credit:
11/12/1996
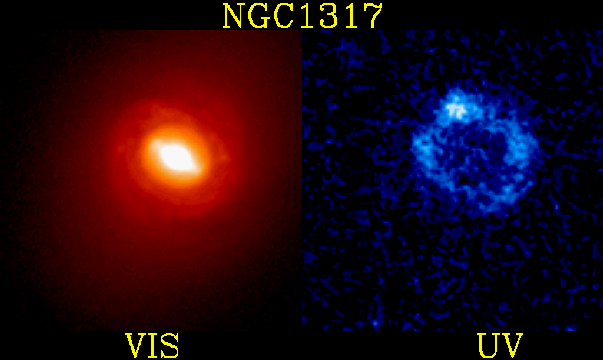
Where do stars form? A typical place is an area of dense nebular gas common to arms in spiral galaxies. Sometimes, however, a burst of star formation can occur with unusual geometry. Nearby galaxy NGC 1317 shows such an unusual ring of star formation surrounding its barred nucleus. In the above image, older stars appear more red and are more evident in the leftmost photograph in visible light. The rightmost photograph taken by the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope is in ultraviolet and highlights stars which are younger and bluer and shows the starbirth ring. This unusual ring may be evidence of a gravitational encounter with another galaxy, causing a density wave to ripple out from the galaxy's center.