Nebula
A nebula is a giant cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and cosmic dust situated between stars in the interstellar medium. Nebulae serve as sites of stellar birth and death—including emission nebulae that glow from ionized gas, reflection nebulae that scatter starlight, and dark nebulae that obscure background stars.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Nebula"
The Butterfly Planetary Nebula
21/10/1997
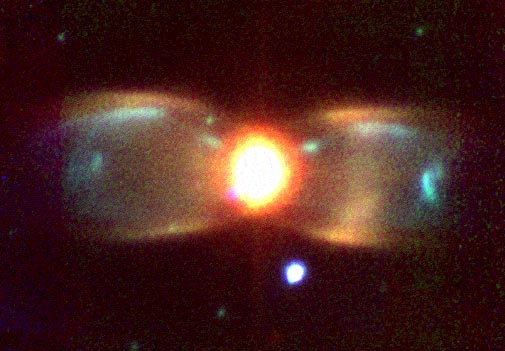
As stars age, they throw off their outer layers. Sometimes a highly symmetric gaseous planetary nebula is created, as is the case in M2-9, also called the Butterfly. Most planetary nebulae show this bipolar appearance, although some appear nearly spherical. An unusual characteristic of the Butterfly is that spots on the "wings" appear to have moved slightly over the years. The above picture was taken in three bands of infrared light and computationally shifted into the visible. Much remains unknown about planetary nebulae, including why some appear symmetric, what creates the knots of emission (some known as FLIERS), and how exactly stars create them.