Nebula
A nebula is a giant cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and cosmic dust situated between stars in the interstellar medium. Nebulae serve as sites of stellar birth and death—including emission nebulae that glow from ionized gas, reflection nebulae that scatter starlight, and dark nebulae that obscure background stars.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Nebula"
X-Ray Stars Of Orion
04/02/2000
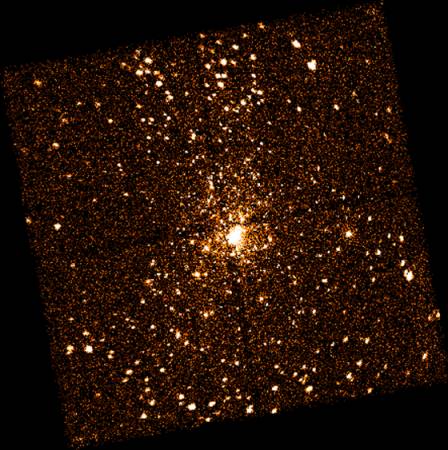
The stars of Orion shine brightly in northern winter skies where the constellation harbors the closest large stellar nursery, the Great Nebula of Orion, a mere 1500 light-years away. In fact, the apparently bright clump of stars near the center of this Chandra X-ray telescope picture of a portion of the nebula are the massive stars of the Trapezium - the young star cluster which powers much of the nebula's visible-light glow. But the sheer number of other stars seen in this X-ray image, which spans about 10 light-years, has surprised and delighted astronomers and this picture was recently touted as the richest field of X-ray sources ever recorded in a single observation. The picture does dramatically illustrate that young stars are prodigious sources of X-rays, thought to be produced in hot stellar coronas and surface flares in a young star's strong magnetic field. Our middle-aged Sun itself was probably thousands of times brighter in X-rays when, like the Trapezium stars, it was only a few million years old. The dark lines through the image are instrumental artifacts.