Nebula
A nebula is a giant cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and cosmic dust situated between stars in the interstellar medium. Nebulae serve as sites of stellar birth and death—including emission nebulae that glow from ionized gas, reflection nebulae that scatter starlight, and dark nebulae that obscure background stars.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Nebula"
At the Edge of the Crescent Nebula
02/08/2000
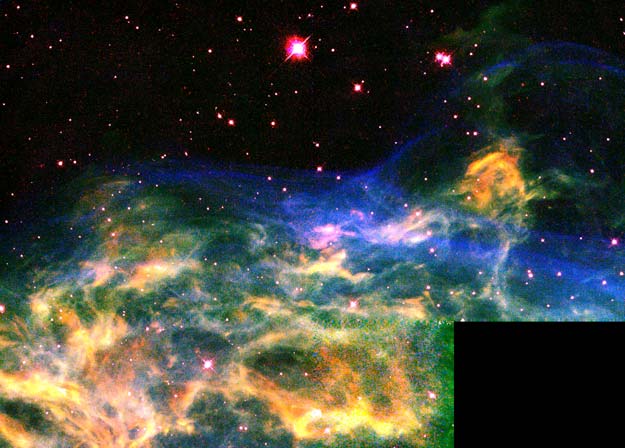
The Crescent Nebula is a rapidly expanding shell of gas surrounding a dying star. In this recently released image by the Hubble Space Telescope, a bright dynamic part of the nebula three light-years across is shown in representative color. The Crescent Nebula began to form about 250,000 years ago as central Wolf-Rayet star WR 136 began to shed its outer envelope in a strong stellar wind, expelling the equivalent of our Sun's mass every 10,000 years. This wind has been impacting surrounding interstellar gas, compacting it into a series of complex shells, and lighting it up. The Crescent Nebula, also known as NGC 6888, lies about 4,700 light-years away in the constellation of Cygnus and can only be seen through a telescope. Star WR 136 will probably undergo a supernova explosion sometime in the next million years.