Nebula
A nebula is a giant cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and cosmic dust situated between stars in the interstellar medium. Nebulae serve as sites of stellar birth and death—including emission nebulae that glow from ionized gas, reflection nebulae that scatter starlight, and dark nebulae that obscure background stars.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Nebula"
NGC 6888: X-Rays in the Wind
16/10/2003
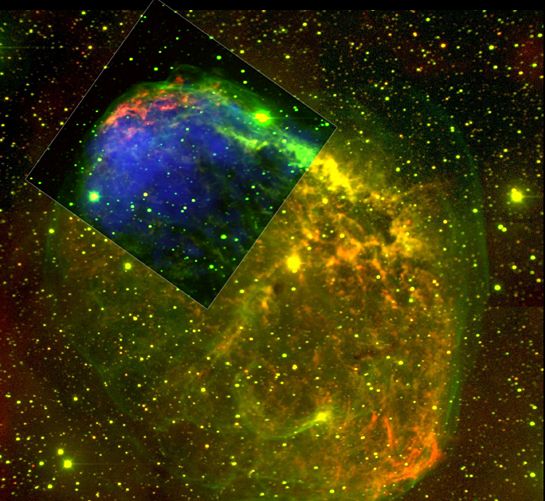
NGC 6888, also known as the Crescent Nebula, is a cosmic bubble of interstellar gas about 25 light-years across. Created by winds from the bright, massive star seen near the center of this composite image, the shocked filaments of gas glowing at optical wavelengths are represented in green and yellowish hues. X-ray image data from a portion of the nebula viewed by the Chandra Observatory is overlaid in blue. Such isolated stellar wind bubbles are not usually seen to produce energetic x-rays, which require heating gas to a million degrees celsius. Still, NGC 6888 seems to have accomplished this as slow moving winds from the central star's initial transition to a red supergiant were overtaken and rammed by faster winds driven by the intense radiation from the star's exposed inner layers. Burning fuel at a prodigious rate and near the end of its stellar life, NGC 6888's central star should ultimately go out with a bang, creating a supernova explosion in 100,000 years or so. NGC 6888 is about 5,000 light-years close, toward the constellation Cygnus.