Nebula
A nebula is a giant cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and cosmic dust situated between stars in the interstellar medium. Nebulae serve as sites of stellar birth and death—including emission nebulae that glow from ionized gas, reflection nebulae that scatter starlight, and dark nebulae that obscure background stars.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Nebula"
In the Center of the Trifid Nebula
30/06/2008
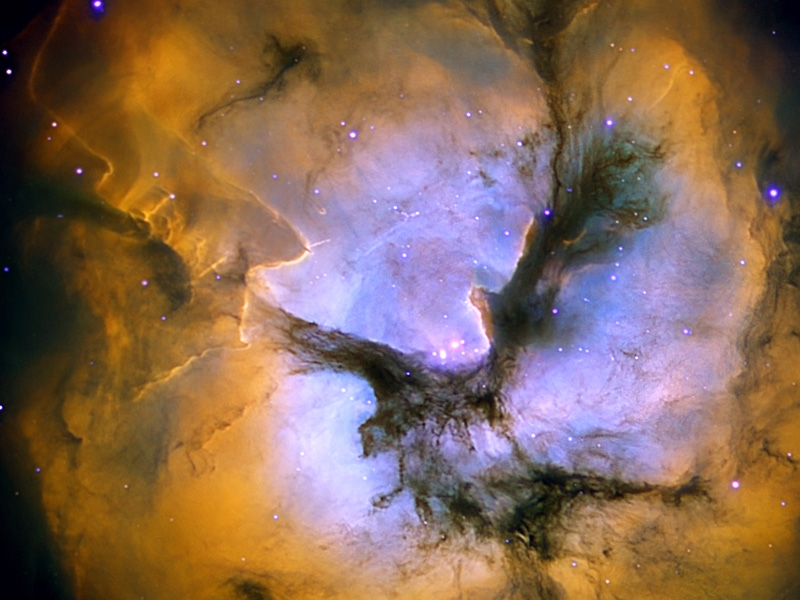
Clouds of glowing gas mingle with dust lanes in the Trifid Nebula, a star forming region toward the constellation of Sagittarius. In the center, the three prominent dust lanes that give the Trifid its name all come together. Mountains of opaque dust appear on the right, while other dark filaments of dust are visible threaded throughout the nebula. A single massive star visible near the center causes much of the Trifid's glow. The Trifid, also known as M20, is only about 300,000 years old, making it among the youngest emission nebulae known. The nebula lies about 9,000 light years away and the part pictured here spans about 10 light years. This image was created with the 0.8-meter IAC80 telescope on the Canary Islands of Spain.