Nebula
A nebula is a giant cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and cosmic dust situated between stars in the interstellar medium. Nebulae serve as sites of stellar birth and death—including emission nebulae that glow from ionized gas, reflection nebulae that scatter starlight, and dark nebulae that obscure background stars.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Nebula"
M57: The Ring Nebula from Hubble
17/08/2021
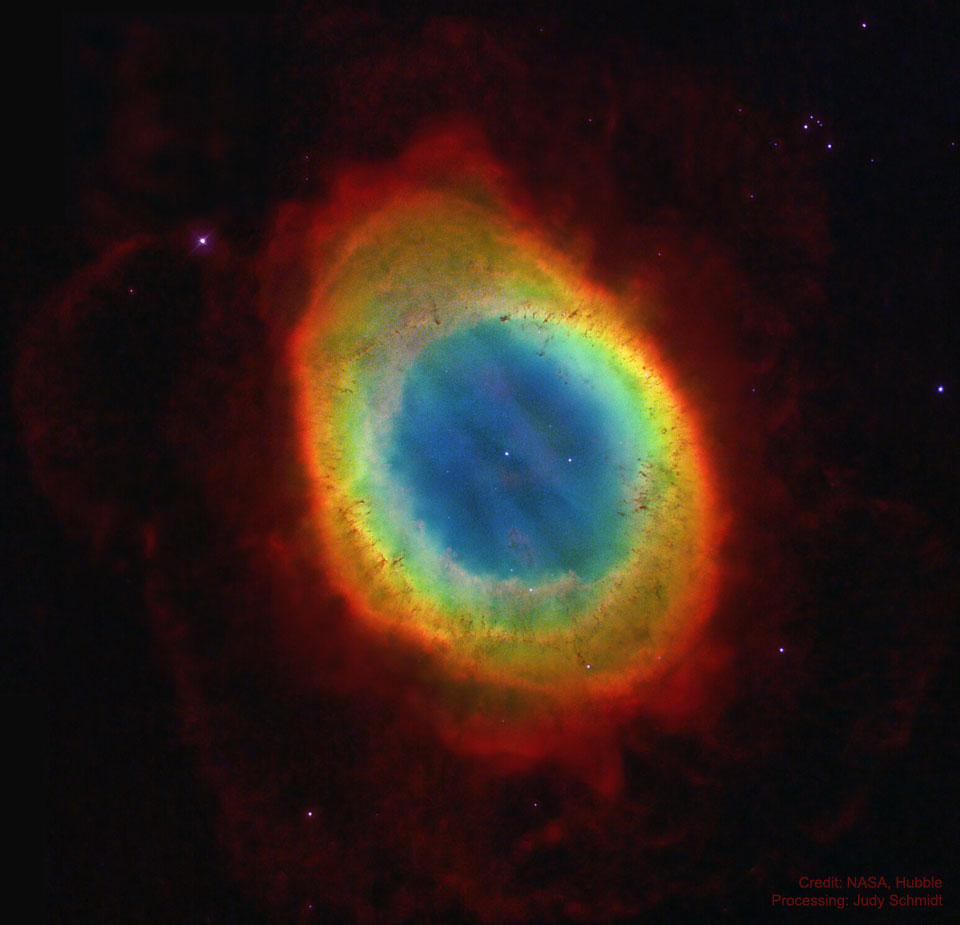
cept for the rings of Saturn, the Ring Nebula (M57) is probably the most famous celestial circle. Its classic appearance is understood to be due to our own perspective, though. The recent mapping of the expanding nebula's 3-D structure, based in part on this clear Hubble image,indicates that the nebula is a relatively dense, donut-like ring wrapped around the middle of a (American) football-shaped cloud of glowing gas. The view from planet Earth looks down the long axis of the football, face-on to the ring. Of course, in this well-studied example of a planetary nebula, the glowing material does not come from planets. Instead, the gaseous shroud represents outer layers expelled from the dying, once sun-like star, now a tiny pinprick of light seen at the nebula's center. Intense ultraviolet light from the hot central star ionizes atoms in the gas. The Ring Nebula is about one light-year across and 2,500 light-years away. Share the Sky: NASA Open API for APOD