Nebula
A nebula is a giant cloud of gas (mostly hydrogen and helium) and cosmic dust situated between stars in the interstellar medium. Nebulae serve as sites of stellar birth and death—including emission nebulae that glow from ionized gas, reflection nebulae that scatter starlight, and dark nebulae that obscure background stars.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Nebula"
Edwin Hubble Discovers the Universe
06/10/2023
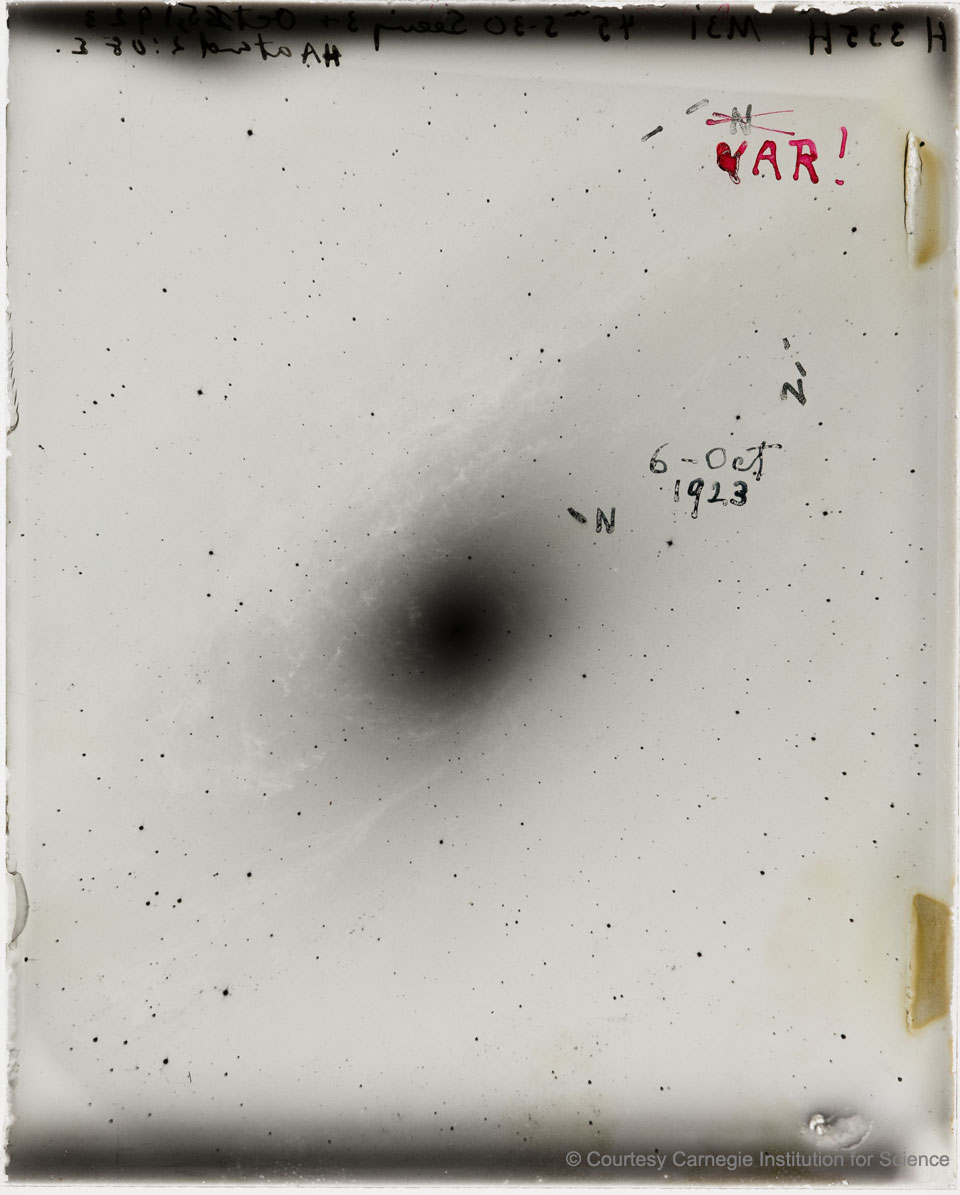
How big is our universe? This question, among others, was debated by two leading astronomers in 1920 in what has since become known as astronomy's Great Debate. Many astronomers then believed that our Milky Way Galaxy was the entire universe. Many others, though, believed that our galaxy was just one of many. In the Great Debate, each argument was detailed, but no consensus was reached. The answer came over three years later with the detected variation of single spot in the Andromeda Nebula, as shown on the original glass discovery plate digitally reproduced here. When Edwin Hubble compared images, he noticed that this spot varied, and on October 6, 1923 wrote "VAR!" on the plate. The best explanation, Hubble knew, was that this spot was the image of a variable star that was very far away. So M31 was really the Andromeda Galaxy -- a galaxy possibly similar to our own. Annotated 100 years ago, the featured image may not be pretty, but the variable spot on it opened a window through which humanity gazed knowingly, for the first time, into a surprisingly vast cosmos.