Perihelion
Perihelion is the point in the orbit of a planet or other celestial body where it is closest to the Sun. For Earth, perihelion occurs annually in early January, when the planet is about 147 million kilometers (91 million miles) from the Sun.
Source: ssd.jpl.nasa.gov
APODs including "Perihelion"
Comet Kudo-Fujikawa: Days in the Sun
30/01/2003
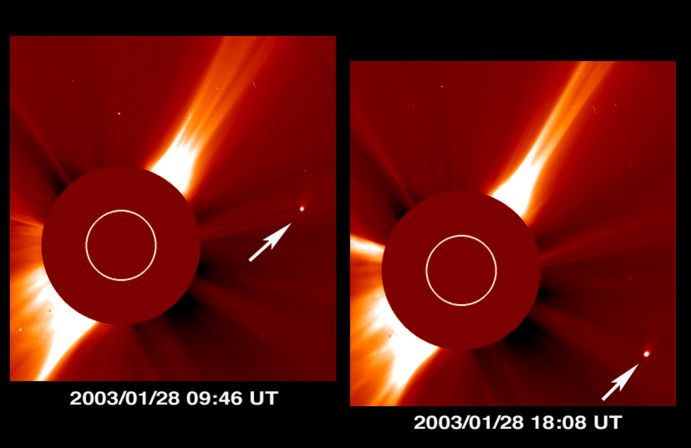
Cruising through the inner Solar System, new Comet Kudo-Fujikawa reached perihelion, its closest approach to the Sun, yesterday, January 29. Passing within 28.4 million kilometers of the Sun, this comet came much closer than innermost planet Mercury basking only 57.9 million kilometers from our parent star. So close to the Sun, comet Kudo-Fujikawa was extremely bright but impossible for earthbound observers to see against the solar glare. Still, the space-based SOHO observatory captured these views of the comet as it neared perihelion by using a coronograph's occulting disk to block the overwhelming sunlight. In the series of images, the size and location of the blocked-out Sun is indicated by white circles, while arrows point to the traveling comet's bright coma and developing tail. Though fading on its outbound journey, Kudo-Fujikawa should soon be visible to southern hemisphere comet-watchers in February's evening skies.