Planetary Nebula
An expanding shell of ionized gas ejected from a red giant star in the late stages of stellar evolution. Despite the name, it has no connection to planets. The glowing gas is illuminated by the hot core of the dying star.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Planetary Nebula"
Fliers Around the Blue Snowball Nebula Credit:
22/11/1996
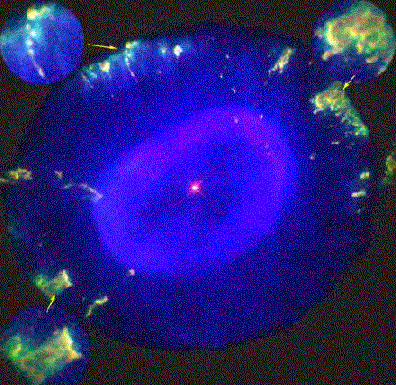
Planetary nebulae are strange. First, they are gas clouds and have nothing to do with our Solar System's planets. Next, although hundreds of planetary nebulae have been catalogued and thousands surely exist in our Galaxy, aspects of the formation process are still debated. But now yet another mystery has come to light: what created the fast-moving gas clouds that appear around planetary nebula? Dubbed FLIERs for Fast Low-Ionization Emission Regions, these knots of dense gas appear to have been ejected from the central star before it cast of the planetary nebula. Currently, no model can account for either their formation or longevity. In the above false-color picture of NGC 7662, the Blue Snowball Planetary Nebula, the FLIERs are featured in the image inserts.