Polaris
Polaris, also known as the North Star, is a multiple-star system located nearly at the North Celestial Pole in the constellation Ursa Minor. Its brightest component, Polaris A, is a classical Cepheid variable supergiant approximately 430 light-years from Earth. The system appears nearly fixed in the sky, making it an important navigational reference.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Polaris"
South Pole Star Trails
02/08/2012
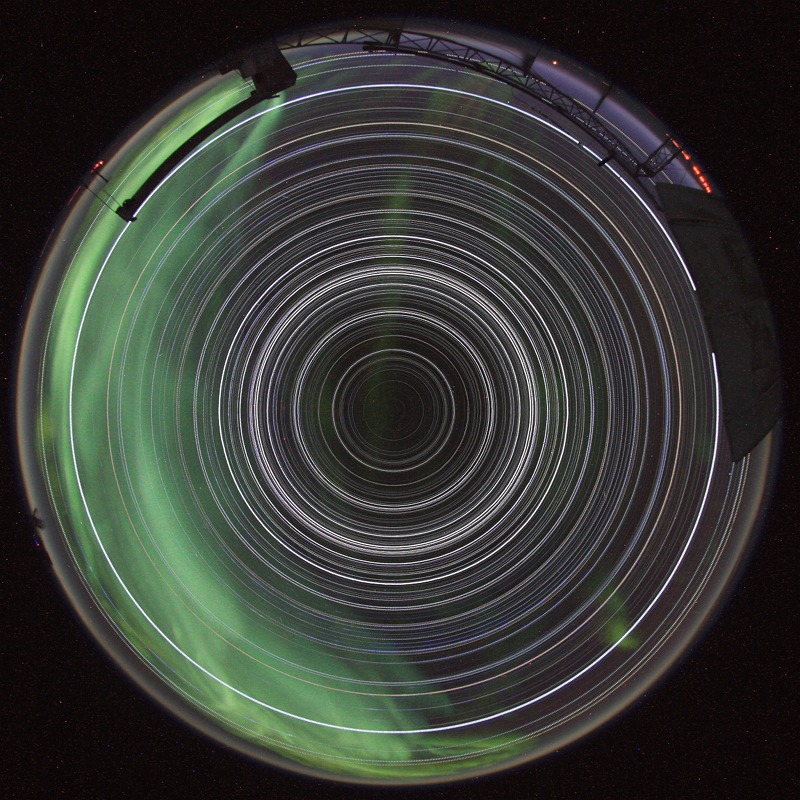
No star dips below the horizon and the Sun never climbs above it in this remarkable image of 24 hour long star trails. Showing all the trails as complete circles, such an image could be achieved only from two places on planet Earth. This example was recorded during the course of May 1, 2012, the digital camera in a heated box on the roof of MAPO, the Martin A. Pomerantz Observatory at the South Pole. Directly overhead in the faint constellation Octans is the projection of Earth's rotational axis, the South Celestial Pole, at the center of all the star trail circles. Not so well placed as Polaris and the North Celestial Pole, the star leaving the small but still relatively bright circle around the South Celestial Pole is Beta Hydri. The inverted umbrella structure on the horizon at the right of the allsky field of view is the ground shield for the SPUD telescope. A shimmering apparition of the aurora australis also visited on this 24 hour night.