Red Giant
A late evolutionary stage of a medium-mass star where the outer layers expand and cool after hydrogen fusion in the core ceases. Red giants can eventually shed their outer envelopes, forming planetary nebulae.
Source: esa.int
APODs including "Red Giant"
TT Cygni: Carbon Star
04/03/2001
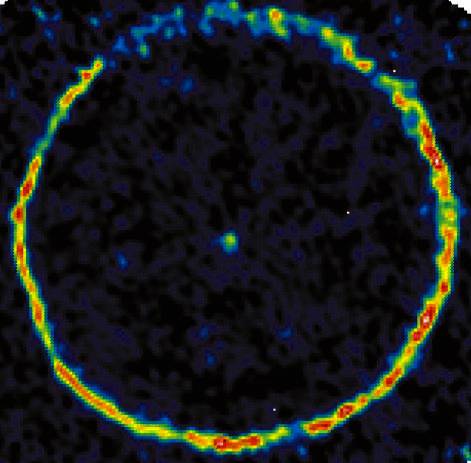
TT Cygni is a cool red giant star with a wind. This false-color picture of TT Cyg was made using a coordinated array of millimeter wavelength radio telescopes and shows radio emission from carbon monoxide (CO) molecules in the surrounding gas. The central emission is from material blown off the red giant over a few hundred years while the thin ring, with a radius of about 1/4 light-year, actually represents a shell of gas expanding outward for 6,000 years. Carbon stars like TT Cyg are so named for their apparent abundance of carbon containing molecules. The carbon is likely the dredged-up ashes of nuclear helium burning in the stellar interior. Carbon stars lose a significant fraction of their total mass in the form of a stellar wind which ultimately enriches the interstellar gas - the source of material for future generations of stars. TT Cyg is about 1,500 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus.