Redshift
Redshift is the phenomenon where light from distant galaxies is stretched to longer, redder wavelengths due to the expansion of the universe. It serves as a key observational evidence for the universe's ongoing expansion.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "Redshift"
The Lyman Alpha Forest
26/01/2003
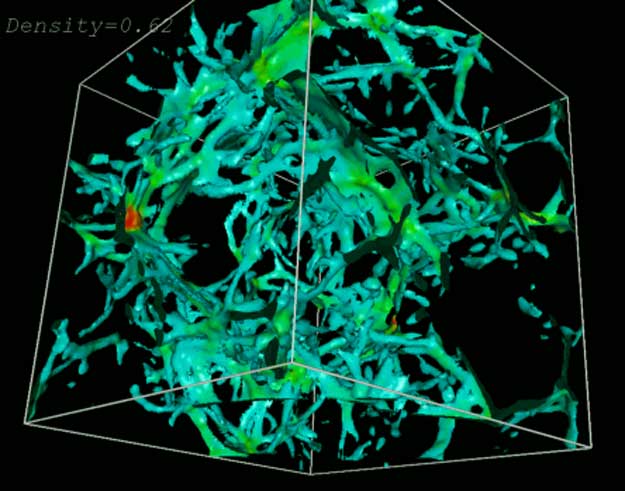
We live in a forest. Strewn throughout the universe are "trees" of hydrogen gas that absorb light from distant objects. These gas clouds leave numerous absorption lines in a distant quasar's spectra, together called the Lyman-alpha forest. Distant quasars appear to be absorbed by many more Lyman-alpha clouds than nearby quasars, indicating a Lyman-alpha thicket early in our universe. The above image depicts one possible computer realization of how Lyman-alpha clouds were distributed at a redshift of 3. Each side of the box measures 30 million light-years across. Much remains unknown about the Lyman-alpha forest, including the real geometry and extent of the clouds, and why there are so many fewer clouds today.