Sagittarius
Sagittarius is a constellation in the southern sky that lies in the direction of the center of the Milky Way galaxy. It is rich in deep-sky objects and is home to Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the Milky Way’s core.
Source: nasa.gov
APODs including "Sagittarius"
Galactic Center Flicker Indicates Black Hole
10/09/2001
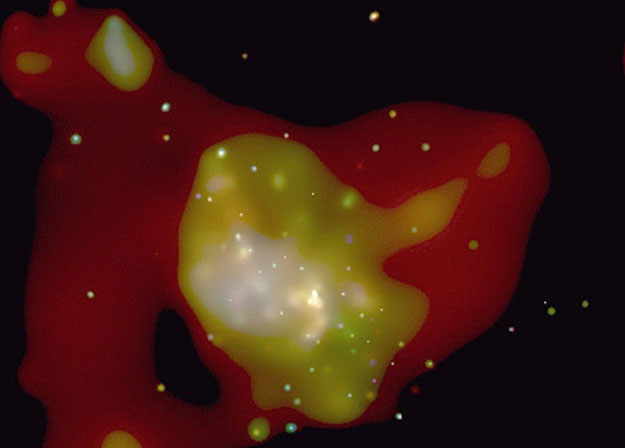
Why would the center of our Galaxy flicker? Many astronomers believe the only credible answer involves a black hole. During observations of Sagittarius A* with the orbiting Chandra X-ray Observatory, the bright X-ray source at the very center of our Milky Way brightened dramatically for a few minutes. Sagittarius A* is visible as the bright dot near the center of the above image. Since large objects cannot vary quickly, a small source is implicated in the variation. Evidence including the motions of central stars indicates that the center of our Galaxy is a massive place, however, estimated to be over a million times the mass of our Sun. Only one known type of object can fit so much mass in so small a volume: a black hole. This short flicker therefore provides additional evidence that a black hole does indeed reside at our Galaxy's center. If true, the flicker might have been caused by an object disrupting as it fell toward the disruptive monster.