Supermassive Black Hole
A black hole with a mass ranging from millions to billions of times that of the Sun, typically found at the centers of galaxies. These black holes influence the dynamics and evolution of their host galaxies.
Source: nasa.gov
APODs including "Supermassive Black Hole"
The Gamma Ray Sky
12/01/2002
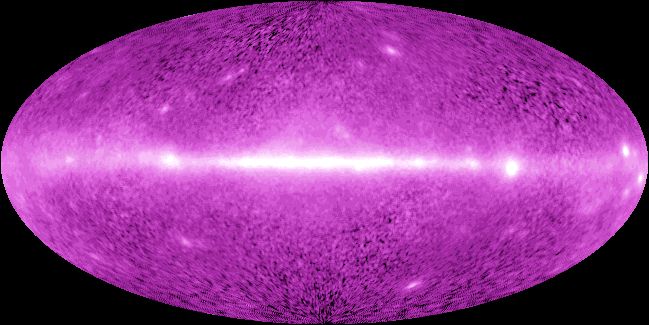
What if you could see gamma rays? If you could, the sky would seem to be filled with a shimmering high-energy glow from the most exotic and mysterious objects in the Universe. In the early 1990s NASA's orbiting Compton Observatory, produced this premier vista of the entire sky in gamma rays, photons with more than 40 million times the energy of visible light. The diffuse gamma-ray glow from the plane of our Milky Way Galaxy runs horizontally through the false-color image. The brightest spots in the galactic plane (right of center) are pulsars, spinning magnetized neutron stars formed in the violent crucibles of stellar explosions. Above and below the plane, quasars, believed to be powered by supermassive black holes, produce gamma-ray beacons at the edges of the universe. The nature of many of the fainter sources remains unknown.