Supermassive Black Hole
A black hole with a mass ranging from millions to billions of times that of the Sun, typically found at the centers of galaxies. These black holes influence the dynamics and evolution of their host galaxies.
Source: nasa.gov
APODs including "Supermassive Black Hole"
NGC 1068 and the X-Ray Flashlight
11/07/2003
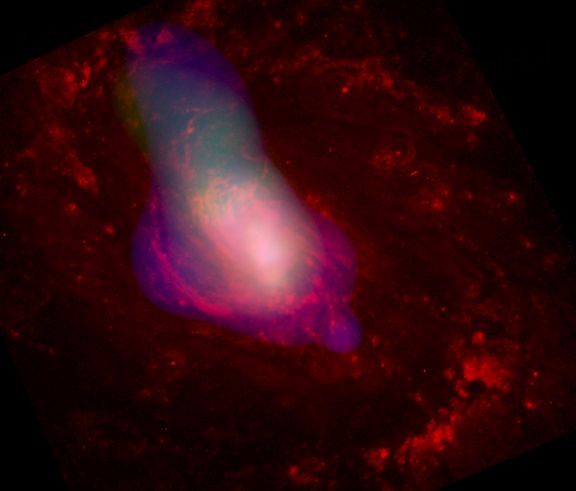
At night, tilting a flashlight up under your chin hides the glowing bulb from the direct view of your friends. Light from the bulb still reflects from your face though, and can give you a startling appearance. Spiral Galaxy NGC 1068 may be playing a similar trick on a cosmic scale, hiding a central powerful source of x-rays -- likely a supermassive black hole -- from direct view. X-rays are still scattered into our line-of-sight though, by a dense torus of material surrounding the black hole. The scenario is supported by x-ray data from the Chandra Observatory combined with a Hubble Space Telescope optical image in this false-color composite picture. Optical data in red shows spiral structure across NGC 1068's inner 7 thousand light-years with the x-ray data overlaid in blue and green. A hot wind of gas streaming from the galaxy's core is seen as the broad swath of x-ray emission while material lit up by the hidden black hole source is within the central cloud of more intense x-rays. Also well known as M77, NGC 1068 lies a mere 50 million light-years away toward the constellation Cetus.