Supernova
A supernova is the explosive death of a star, during which it rapidly ejects most of its mass in a brilliant burst of light. In core‑collapse supernovae (Types Ib, Ic, II), massive stars (≥ 8 solar masses) exhaust their nuclear fuel, collapse under gravity, and explode. In Type Ia supernovae, a white dwarf in a binary system undergoes runaway fusion after accreting mass. These events deliver heavy elements into space, leave behind neutron stars or black holes, and power typical shock‑front supernova remnants.
Source: heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov
APODs including "Supernova"
Cygnus Loop Supernova Shockwave
18/07/1995
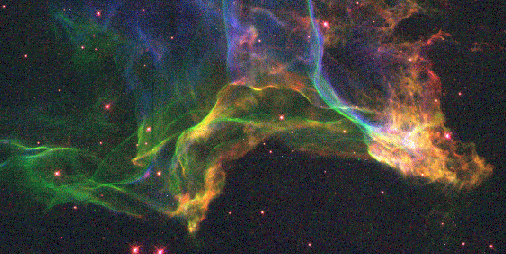
July 18, 1995 Cygnus Loop Supernova Shockwave Credit: NASA, HST, WFPC2, Jeff Hester Explanation: 15,000 years ago a star in the constellation of Cygnus exploded. This picture shows a portion of a shockwave from this supernova explosion still expanding past nearby stars. The collision of this gaseous shockwave with a stationary gas cloud has heated the gas causing it to glow in a spectacular array of colors, known as the Cygnus Loop. This picture was taken with the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 on board the Hubble Space Telescope. For more information see the NASA Hubble Space Telescope press release. We keep an archive of Astronomy Pictures of the Day. Astronomy Picture of the Day is brought to you by Robert Nemiroff and Jerry Bonnell . Original material on this page is copyrighted to Robert J. Nemiroff and Jerry T. Bonnell.