Supernova
A supernova is the explosive death of a star, during which it rapidly ejects most of its mass in a brilliant burst of light. In core‑collapse supernovae (Types Ib, Ic, II), massive stars (≥ 8 solar masses) exhaust their nuclear fuel, collapse under gravity, and explode. In Type Ia supernovae, a white dwarf in a binary system undergoes runaway fusion after accreting mass. These events deliver heavy elements into space, leave behind neutron stars or black holes, and power typical shock‑front supernova remnants.
Source: heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov
APODs including "Supernova"
M1: Polarization of the Crab
23/11/1995
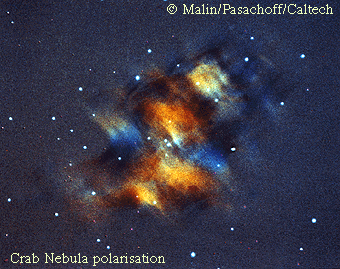
The Crab Nebula resulted from a star that exploded - a supernova. Although the stellar explosion that caused the Crab Nebula was seen over 900 years ago, the nebula itself still expands and shines. Much of the emitted light has been found to be polarized. Light waves with the same polarization vibrate in the same plane. Light waves can be polarized by reflection from a surface, an effect familiar to sunglass wearing fishermen and skiers. Polarized light can also be emitted by regions that contain strong magnetic fields. Areas of different polarization above are highlighted by different colors. Mapping the polarization helps astronomers decipher which physical processes create the observed light.