Supernova
A supernova is the explosive death of a star, during which it rapidly ejects most of its mass in a brilliant burst of light. In core‑collapse supernovae (Types Ib, Ic, II), massive stars (≥ 8 solar masses) exhaust their nuclear fuel, collapse under gravity, and explode. In Type Ia supernovae, a white dwarf in a binary system undergoes runaway fusion after accreting mass. These events deliver heavy elements into space, leave behind neutron stars or black holes, and power typical shock‑front supernova remnants.
Source: heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov
APODs including "Supernova"
The Case of the Missing Supernova
13/04/1999
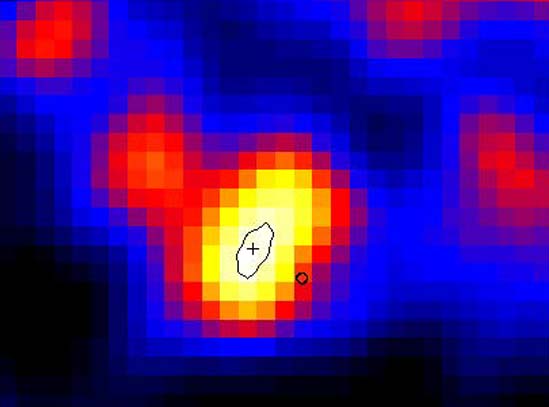
Would you notice a second Moon in the sky? About 700 years ago, light from a tremendous explosion reached Earth that should have appeared almost as bright as a full Moon. The bright spot should have lasted for weeks, yet no notation of such an occurrence has been found in historical records. The mystery was uncovered by Wan Chen and Neil Gehrels (NASA/GSFC) when studying the source of radioactive elements toward the Vela supernova remnant. They deduced that an explosion much younger and closer than the supernova that caused Vela must have occurred, and even computed explosion characteristics from the amounts of radioactive elements present. They calculate that GRO/RX J0852 should have dazzled medieval stargazers. Perhaps people were too busy, surviving records are too incomplete, or the explosion was somehow too dim. The above picture of GRO/RX J0852 was taken in gamma-ray light with the Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory and is shown in false-color. Astronomers and historians continue to contemplate the clues.