Supernova
A supernova is the explosive death of a star, during which it rapidly ejects most of its mass in a brilliant burst of light. In core‑collapse supernovae (Types Ib, Ic, II), massive stars (≥ 8 solar masses) exhaust their nuclear fuel, collapse under gravity, and explode. In Type Ia supernovae, a white dwarf in a binary system undergoes runaway fusion after accreting mass. These events deliver heavy elements into space, leave behind neutron stars or black holes, and power typical shock‑front supernova remnants.
Source: heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov
APODs including "Supernova"
NGC 3603: X-Rays From A Starburst Cluster
24/01/2001
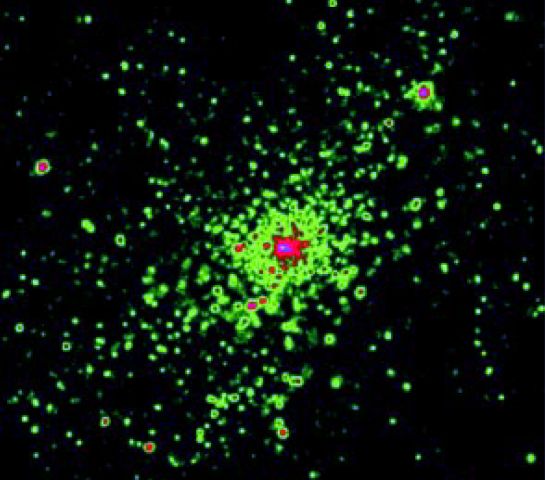
A mere 20,000 light-years from the Sun lies the NGC 3603 star cluster, a resident of the nearby Carina spiral arm of our Milky Way galaxy. Seen here in this recent false-color x-ray image from the Chandra Observatory, NGC 3603 is well known to astronomers as a young cluster in a large galactic star-forming region. The image colors were chosen to show the relative x-ray brightness of the many individual sources present, where green are faint and red to purple hues are bright sources of x-rays. The stars in the cluster were formed in a single "burst" of star formation only one or two million years ago, so the x-rays are believed to come from the massive young stars themselves or from their energetic stellar winds. Since other common galactic sources of x-rays such as supernova remnants and neutron stars represent final stages in the life of a massive star, they are unlikely to be present in such a young cluster. Nearby NGC 3603 is thought to be a convenient example of the star clusters that populate distant starburst galaxies.