Supernova
A supernova is the explosive death of a star, during which it rapidly ejects most of its mass in a brilliant burst of light. In core‑collapse supernovae (Types Ib, Ic, II), massive stars (≥ 8 solar masses) exhaust their nuclear fuel, collapse under gravity, and explode. In Type Ia supernovae, a white dwarf in a binary system undergoes runaway fusion after accreting mass. These events deliver heavy elements into space, leave behind neutron stars or black holes, and power typical shock‑front supernova remnants.
Source: heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov
APODs including "Supernova"
X-Rays From Tycho's Supernova Remnant
12/09/2002
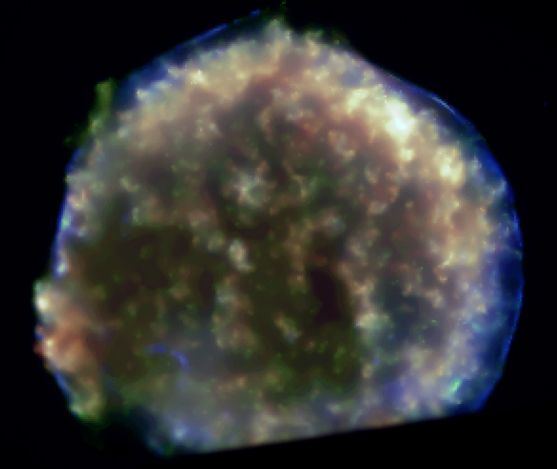
In 1572, Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe recorded the sudden appearance of a bright new star in the constellation Cassiopeia. The new star faded from view over a period of months and is believed to have been a supernova, one of the last stellar explosions seen in our Milky Way galaxy. Now known as Tycho's Supernova Remnant, the expanding debris cloud is shown in this detailed false-color x-ray image from the orbiting Chandra Observatory. Represented in blue, the highest energy x-rays come from shocked regions along the outer edges of the supernova remnant, corresponding to gas at temperatures of 20 million degrees Celsius. X-rays from cooler gas (only 10 million degrees or so!) dominate the remnant's interior. Unlike some other supernova remnants, no hot central point source can be found, supporting the theory that the origin of this stellar explosion was a runaway nuclear detonation that ultimately destroyed a white dwarf star. At a distance of about 7,500 light-years, Tycho's Supernova Remnant appears to be nearly 20 light-years across. This x-ray picture's field of view slightly cuts off the bottom of the generally spherical cloud.