Supernova
A supernova is the explosive death of a star, during which it rapidly ejects most of its mass in a brilliant burst of light. In core‑collapse supernovae (Types Ib, Ic, II), massive stars (≥ 8 solar masses) exhaust their nuclear fuel, collapse under gravity, and explode. In Type Ia supernovae, a white dwarf in a binary system undergoes runaway fusion after accreting mass. These events deliver heavy elements into space, leave behind neutron stars or black holes, and power typical shock‑front supernova remnants.
Source: heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov
APODs including "Supernova"
The Expanding Light Echoes of SN 1987A
25/01/2006
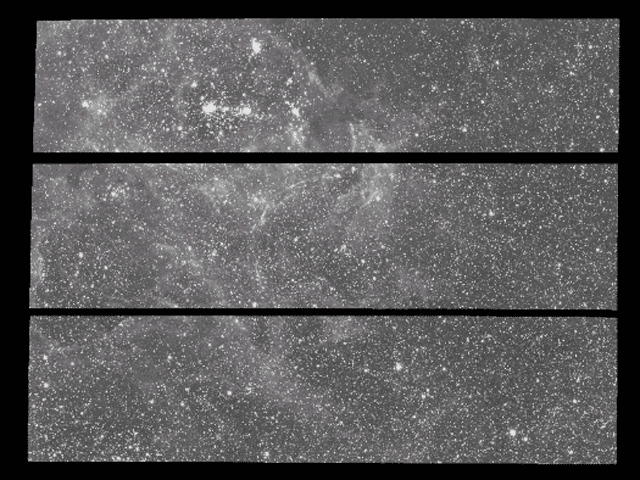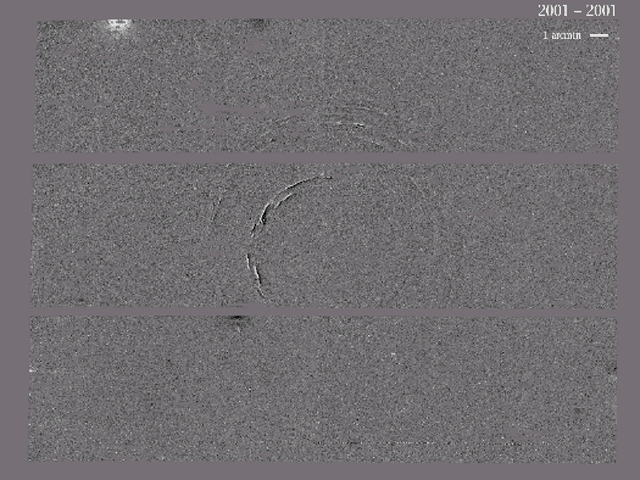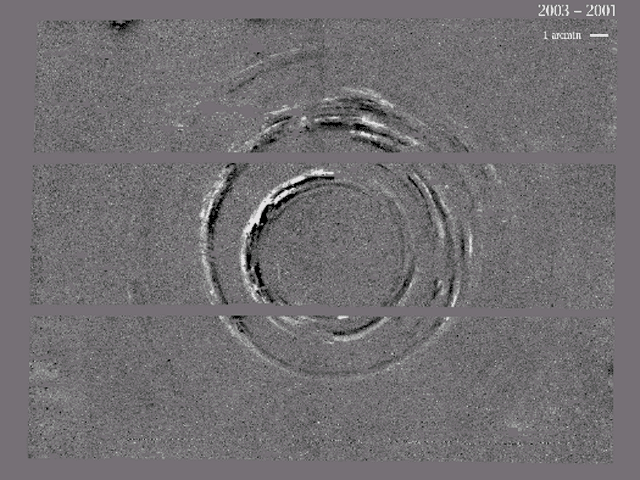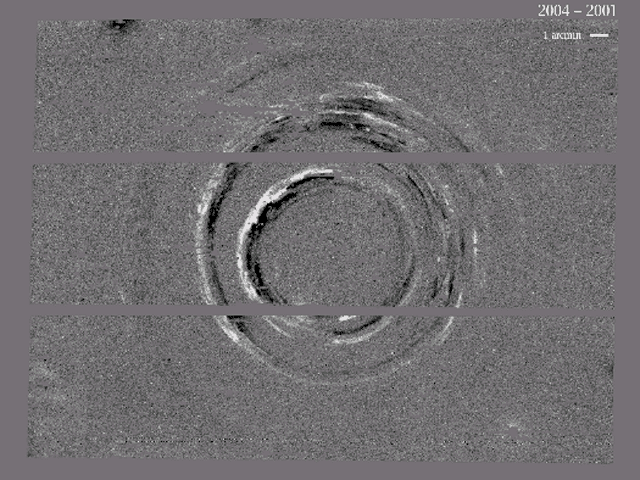
Can you find supernova 1987A? It isn't hard -- it occurred at the center of the expanding bullseye pattern. Although this stellar detonation was first seen almost two decades ago, light from it continues to bounce off clumps of interstellar dust and be reflected to us today. These expanding light echoes have been recorded in the above time-lapse movie recorded over four years from the Blanco 4-meter telescope in Chile. The first image is an image of the SN 1987A region, while the next four images were created by subtracting consecutive images, taken a year apart, and leaving only the difference between the images. Light echoes can be seen moving out from the position of the supernova. The SuperMACHO team who recorded the above light echoes around supernova 1987A has also found faint and previously unnoticed light echoes from two other LMC supernovas. Study of these light echoes has enabled more accurate determinations of the location and date of these two supernova explosions that were first visible hundreds of years ago.