Supernova
A supernova is the explosive death of a star, during which it rapidly ejects most of its mass in a brilliant burst of light. In core‑collapse supernovae (Types Ib, Ic, II), massive stars (≥ 8 solar masses) exhaust their nuclear fuel, collapse under gravity, and explode. In Type Ia supernovae, a white dwarf in a binary system undergoes runaway fusion after accreting mass. These events deliver heavy elements into space, leave behind neutron stars or black holes, and power typical shock‑front supernova remnants.
Source: heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov
APODs including "Supernova"
The Changing Surface of Fading Betelgeuse
17/02/2020
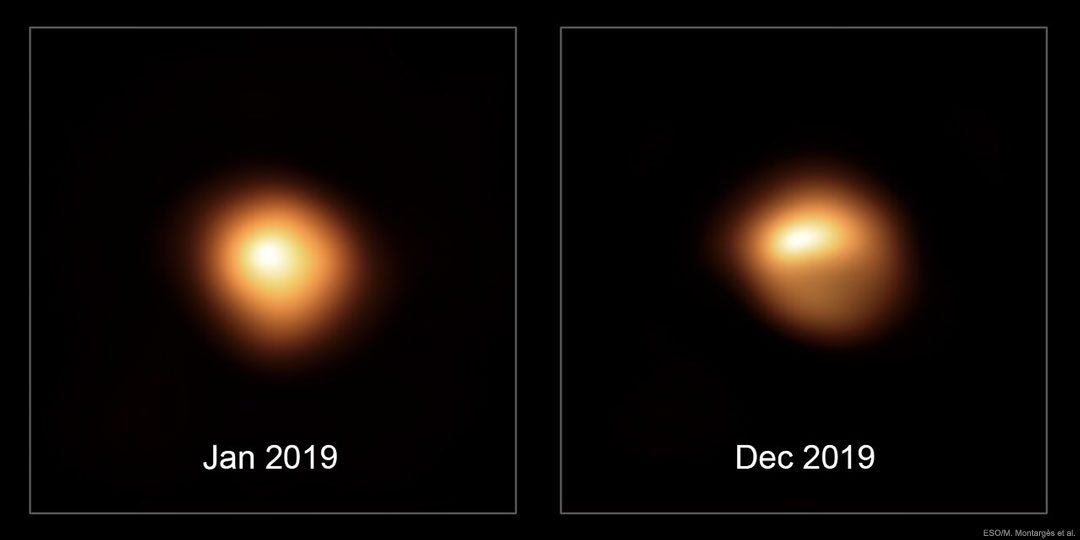
Besides fading, is Betelgeuse changing its appearance? Yes. The famous red supergiant star in the familiar constellation of Orion is so large that telescopes on Earth can actually resolve its surface -- although just barely. The two featured images taken with the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope show how the star's surface appeared during the beginning and end of last year. The earlier image shows Betelgeuse having a much more uniform brightness than the later one, while the lower half of Betelgeuse became significantly dimmer than the top. Now during the first five months of 2019 amateur observations show Betelgeuse actually got slightly brighter, while in the last five months the star dimmed dramatically. Such variability is likely just normal behavior for this famously variable supergiant, but the recent dimming has rekindled discussion on how long it may be before Betelgeuse does go supernova. Since Betelgeuse is about 700 light years away, its eventual supernova -- probably thousands of years in the future -- will likely be an amazing night-sky spectacle, but will not endanger life on Earth.