Supernova
A supernova is the explosive death of a star, during which it rapidly ejects most of its mass in a brilliant burst of light. In core‑collapse supernovae (Types Ib, Ic, II), massive stars (≥ 8 solar masses) exhaust their nuclear fuel, collapse under gravity, and explode. In Type Ia supernovae, a white dwarf in a binary system undergoes runaway fusion after accreting mass. These events deliver heavy elements into space, leave behind neutron stars or black holes, and power typical shock‑front supernova remnants.
Source: heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov
APODs including "Supernova"
Supernova Remnant: The Veil Nebula
22/06/2022
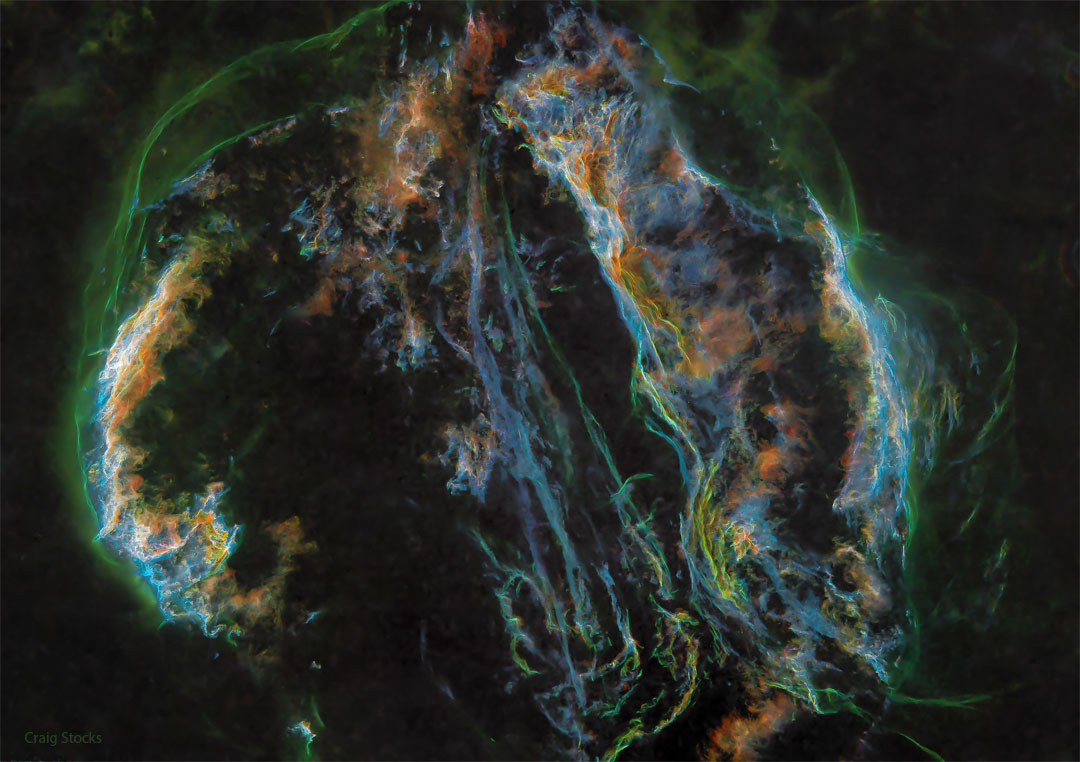
Ten thousand years ago, before the dawn of recorded human history, a new light would have suddenly have appeared in the night sky and faded after a few weeks. Today we know this light was from a supernova, or exploding star, and record the expanding debris cloud as the Veil Nebula, a supernova remnant. Imaged with color filters featuring light emitted by sulfur (red), hydrogen (green), and oxygen (blue), this deep wide-angle view was processed to remove the stars and so better capture the impressive glowing filaments of the Veil. Also known as the Cygnus Loop, the Veil Nebula is roughly circular in shape and covers nearly 3 degrees on the sky toward the constellation of the Swan (Cygnus). Famous nebular sections include the Bat Nebula, the Witch's Broom Nebula, and Fleming's Triangular Wisp. The complete supernova remnant lies about 1,400 light-years away.