The Moon
The Moon is Earth’s only natural satellite—a rocky, cratered body about one‑quarter the diameter of Earth, orbiting at an average distance of approximately 384,400 km. It influences tides, stabilizes Earth’s axial tilt, and was formed about 4.5 billion years ago following a collision between Earth and a Mars-sized object.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Moon"
Shadow at the Lunar South Pole
28/11/1995
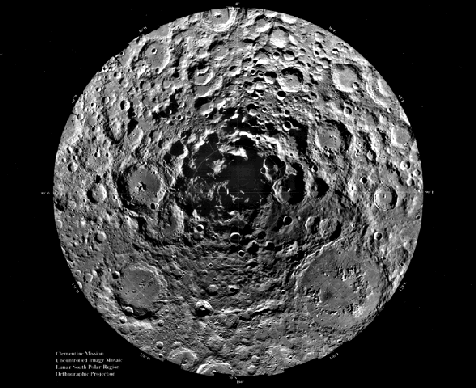
In 1994, the space probe Clementine spent 70 days in lunar orbit mapping the Moon's surface. Shown above is a dramatically detailed composite view centered on the Moon's South Pole constructed from 1500 Clementine images. The top half shows the part of the Moon which faces the Earth while the bottom half is the lunar Farside. The images reveal a major depression very near the South Pole itself, probably caused by the impact of a comet or asteroid. The shadow region near the impact site is extensive and may be permanent - creating an area cold enough to trap water of cometary origin as ice.