The Moon
The Moon is Earth’s only natural satellite—a rocky, cratered body about one‑quarter the diameter of Earth, orbiting at an average distance of approximately 384,400 km. It influences tides, stabilizes Earth’s axial tilt, and was formed about 4.5 billion years ago following a collision between Earth and a Mars-sized object.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Moon"
Ring of Fire from Cape Wrath
05/06/2003
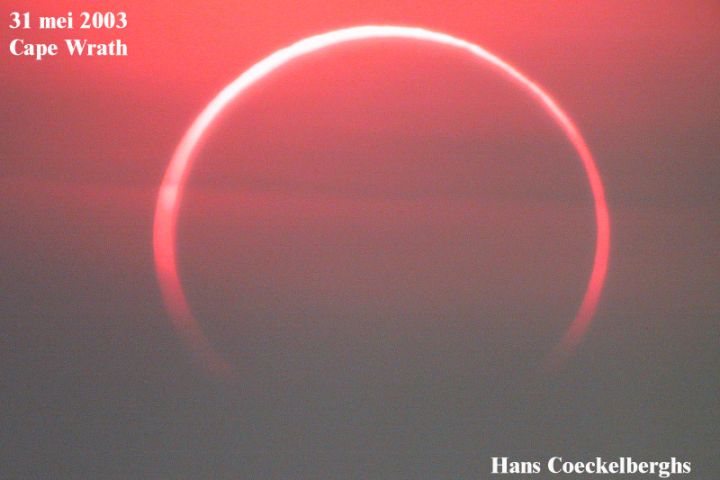
If the Moon's apparent diameter is not quite large enough to cover the Sun during a solar eclipse, an annular eclipse can be the result -- a spectacle of silhouetted Moon surrounded by a solar "ring of fire". Just such a view was possible for observers in the far northern hemisphere as the new Moon slid across the solar disk on May 31st. Still, for astronomical adventurers at Cape Wrath on the northwestern coast of Scotland, the eastern sky was cloudy on eclipse day. But fortunately the Sun became visible a few minutes prior to the annular phase and determined astronomer Hans Coeckelberghs was able to capture this dramatic telescopic image of the eclipsed Sun's ring of fire looming through a reddened, cloud-streaked sky. Not to be outdone by the north, the far southern hemisphere will host the next solar eclipse, with the path of totality racing across Antarctica on November 23rd.