The Moon
The Moon is Earth’s only natural satellite—a rocky, cratered body about one‑quarter the diameter of Earth, orbiting at an average distance of approximately 384,400 km. It influences tides, stabilizes Earth’s axial tilt, and was formed about 4.5 billion years ago following a collision between Earth and a Mars-sized object.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Moon"
A Rare Annular Venusian Solar Eclipse
15/06/2004
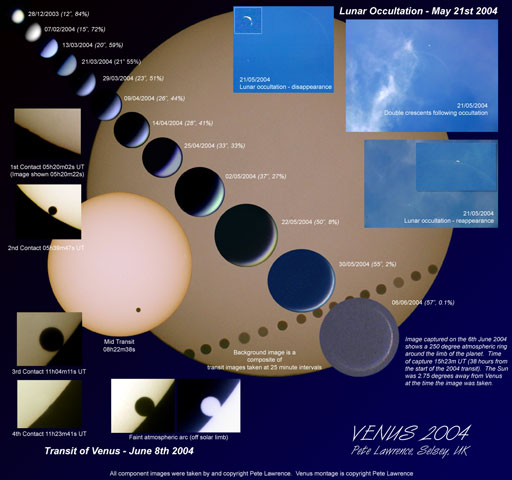
An unusual type of solar eclipse occurred last week. Usually it is the Earth's Moon that eclipses the Sun. Last week, for the first time in over 100 years, the planet Venus took a turn. Like a solar eclipse by the Moon, the phase of Venus became a continually thinner crescent as Venus became increasingly better aligned with the Sun. Eventually the alignment became perfect and the phase of Venus dropped to zero. The dark spot of Venus crossed our parent star. The situation could technically be labeled a Venusian annular eclipse with an extraordinarily large ring of fire. From above the thick cloud tops of Venus, the Earth appeared in its fullest phase, brighter in the Venusian sky than even Mars appeared from Earth last August. Hours later, as Venus continued in its orbit, a slight crescent phase appeared again. The next Venusian solar eclipse will occur in 2012.