The Moon
The Moon is Earth’s only natural satellite—a rocky, cratered body about one‑quarter the diameter of Earth, orbiting at an average distance of approximately 384,400 km. It influences tides, stabilizes Earth’s axial tilt, and was formed about 4.5 billion years ago following a collision between Earth and a Mars-sized object.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Moon"
Galactic Magnetar Throws Giant Flare
21/02/2005
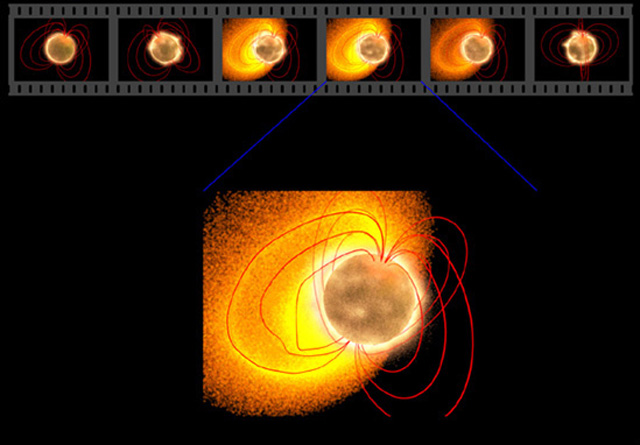
Was the brightest Galactic blast yet recorded a key to connecting two types of celestial explosions? Last December, a dense sheet of gamma rays only a few times wider than the Earth plowed through our Solar System, saturating satellites and noticeably reflecting off the Moon. A magnetar near our Galactic Center, the source of Soft Gamma Repeater (SGR) 1806-20, had unleashed its largest flare on record. The brightness and briefness of the tremendous explosion's initial peak made it look quite similar to another type of tremendous explosion if viewed from further away -- a short duration gamma-ray burst (GRB). Short duration GRBs are thought by many to be fundamentally different than their long duration GRB cousins that are likely related to distant supernovas. Illustrated above is a series of drawings depicting an outgoing explosion during the initial SGR spike. A fast moving wave of radiation is pictured shooting away from a central magnetar. The possible link between SGRs and GRBs should become better understood as more and similar events are detected by the Earth-orbiting Swift satellite.