The Moon
The Moon is Earth’s only natural satellite—a rocky, cratered body about one‑quarter the diameter of Earth, orbiting at an average distance of approximately 384,400 km. It influences tides, stabilizes Earth’s axial tilt, and was formed about 4.5 billion years ago following a collision between Earth and a Mars-sized object.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Moon"
Eclipsed Moon in Infrared
23/04/2005
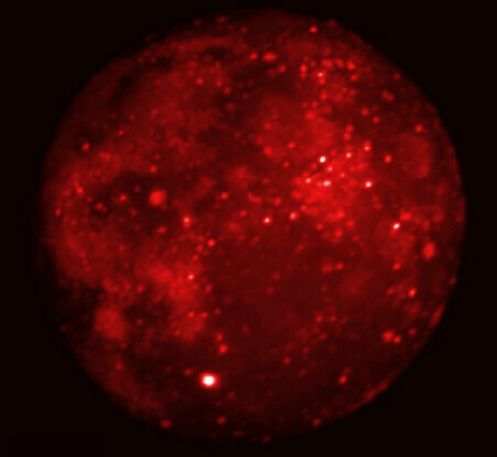
In September of 1996, the Midcourse Space Experiment (MSX) satellite had a spectacular view of a total lunar eclipse from Earth orbit. SPIRIT III, an on board infrared telescope, was used to repeatedly image the moon during the eclipse. Above is one of the images taken during the 70 minute totality, the Moon completely immersed in the Earth's shadow. Infrared light has wavelengths longer than visible light - humans can not see it but feel it as heat. So, the bright spots correspond to the warm areas on the lunar surface, and dark areas are cooler. The brightest spot below and left of center is the crater Tycho, while the dark region at the upper right is the Mare Crisium. Of course, this Sunday's lunar eclipse will not be a total, or even a partial one. Instead, the Moon will glide through the subtle outer portion of the Earth's shadow in a penumbral eclipse of the Moon.