The Moon
The Moon is Earth’s only natural satellite—a rocky, cratered body about one‑quarter the diameter of Earth, orbiting at an average distance of approximately 384,400 km. It influences tides, stabilizes Earth’s axial tilt, and was formed about 4.5 billion years ago following a collision between Earth and a Mars-sized object.
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Moon"
31 Million Miles from Planet Earth
03/09/2008
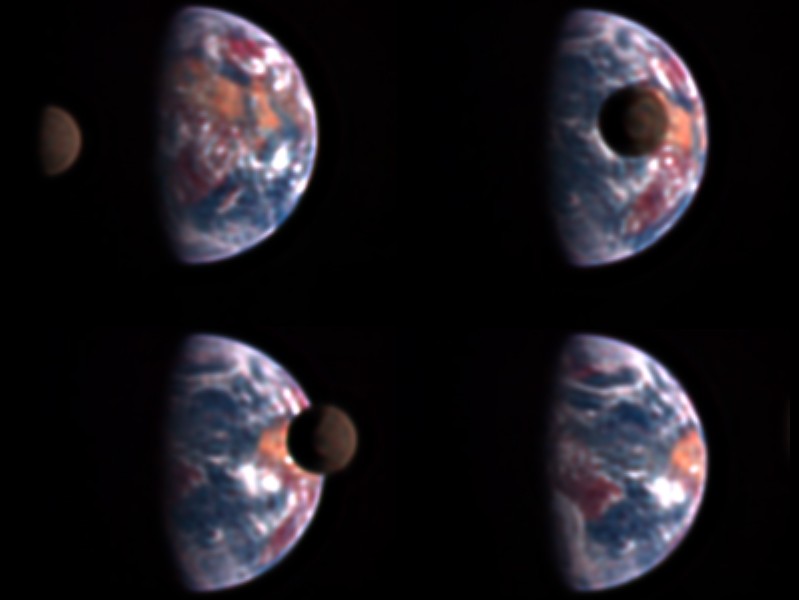
On July 4th, 2005, the Deep Impact spacecraft directed a probe to impact the nucleus of Comet Tempel 1. Still cruising through the solar system, earlier this year the robotic spacecraft looked back to record a series of images of its home world 31 million miles (50 million kilometers) away. In a sequence from top left to bottom right, these four frames from the video show a rotating Earth. They combine visible and near-infrared image data with enough resolution and contrast to see clouds, oceans, and continents. They also follow a remarkable transit of Earth by its large, natural satellite, the Moon. The Moon's orbital motion carries it across the field of view from left to right. Imaging the Earth from this distant perspective allows astronomers to connect overall variations in brightness at different wavelengths with planetary features. The observations will aid in the search for earthlike planets in other planetary systems.