The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
The Sun Erupts
13/08/1995
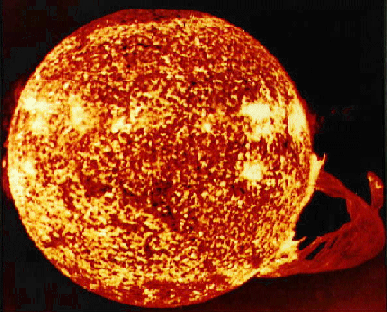
August 13, 1995 The Sun Erupts Credit: NASA, Skylab Explanation: The sun was captured in 1973 throwing one of the largest eruptive prominences ever recorded. Sol, our sun, is a normal star. It formed about 5 billion years ago, and will last about another 5 billion years. The sun will never explode, and a solar flare will never destroy the earth. Eventually the sun will become a white dwarf star. The sun is made of mostly hydrogen and helium. The sun's center is so hot that when hydrogen nuclei collide, they stick together and release energy - a process called nuclear fusion No one knows why the center of the sun emits so few neutrinos.