The Sun
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star (G2V), about 4.6 billion years old, and the dominant gravitational force in the Solar System. It has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers and contains around 99.8% of the Solar System’s mass. Nuclear fusion in its core converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy that warms the planets. Above the core lie the radiative and convective zones, followed by the visible photosphere (~5,500 °C), the chromosphere, and the much hotter corona (~2 million °C).
Source: science.nasa.gov
APODs including "The Sun"
70 Virginis b: A New Water Planet?
30/01/1996
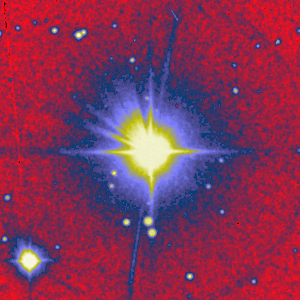
The star 70 Virginis has a planet. This recent discovery is the second known case of a planet orbiting a normal star other than our Sun itself. The first case involved 51 Pegasi and was announced last year. The star 70 Vir, shown in the center of the above false-color picture, is very much like the Sun. The planet is not visible above - the unusual structure surrounding the star is caused by the telescope. The planet, designated 70 Vir b for short, was discovered by very slight periodic shifts in its colors. Defining characteristics of this planet include that it is at least eight times the mass of Jupiter, it's orbit is much smaller than Jupiter's, and it's temperature allows water to exist in liquid form - like on the Earth. Life on Earth is based on liquid water - could life exist here too?